
International Journal of
Environmental Research
and Public Health
Systematic Review
The Effects of Forest Therapy on Immune Function
Youngran Chae 1, Sunhee Lee 2,*, Youngmi Jo 3, Soyean Kang 4, Suyoun Park 5 and Hyoyoung Kang 6
1 College of Nursing, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea; yrchae@kangwon.ac.kr
2 Department of Nursing, Yeoju Institute of Technology, Yeoju-si 12653, Korea
3 Department of Nursing, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon 24289, Korea;
youngs905@hanmail.net
4 Department of Nursing, Daewon University College, Jecheon 27135, Korea; seizy@daewon.ac.kr
5 Department of Nursing, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea; suyoun2419@gmail.com
6 Department of Nursing, Songho College, Heongseong 25242, Korea; sissy2@songho.ac.kr
* Correspondence: baezzang1224@yit.ac.kr
Citation: Chae, Y.; Lee, S.; Jo, Y.;
Kang, S.; Park, S.; Kang, H. The
Effects of Forest Therapy on Immune
Function. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public
Health 2021, 18, 8440. https://
doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168440
Abstract: We conducted a systematic review of the effects of a forest therapy program on adults’
immune function. We used PICO-SD (participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, study
design) to identify key items. The participants were adults over the age of 18 and the intervention
was forest therapy. Our comparisons included studies that comparatively analyzed urban groups
or groups that did not participate in forest therapy intervention. Cases without control groups
were also included. Immunological outcome measures were included in measuring intervention
outcomes. All experimental studies, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), non-equivalent
control group designs (non-RCTs), and one-group pretest-posttest design were included in the study
design. A total of 13 studies were included for comparison. Forest therapy programs were divided
into lodging-type and session-type programs. The representative measures for evaluating the effects
of immune function were the number of NK cells, the cytotoxic activity of NK cells, and cytotoxic
effector molecules. Most studies reported improvement in these measures when comparing values
after intervention with values before the forest therapy intervention. Therefore, forest therapy has
been found to be effective in improving immune function. More RCT studies on the effects of forest
therapy on immune function are necessary.
Keywords: forest therapy; adults; immune function
Academic Editor: Paul B. Tchounwou
Received: 9 July 2021
Accepted: 6 August 2021
Published: 10 August 2021
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral
with regard to jurisdictional claims in
published maps and institutional affil-
iations.
Copyright: © 2021 by the authors.
Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
This article is an open access article
distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons
Attribution (CC BY) license (https://
creativecommons.org/licenses/by/
4.0/).
1. Introduction
Forest therapy creates a state of physical relaxation by exposing a participant to a
natural environment. It is thought to activate compromised immune function and improve
immune function for maintaining and promoting health [1]. Forest therapy makes use
of various elements of the forest environment to help individuals cope with stress and to
maintain and promote their health [1]. As awareness of forest therapy has increased, so
has the number of individuals participating in this therapy [2]. In addition, as stress levels
have escalated and public frustration caused by social distancing mandates during the
COVID-19 pandemic has increased, public interest in forest therapy has also increased.
An increasing number of visitors to forest areas have indicated that COVID-19 was the
motivation behind their forest visit [3].
In line with this trend, there has been a steady increase in studies investigating and
verifying the effects of forest therapy [4–10]. Numerous studies have reported that forest
therapy can have positive effects on physical and psychological health [4–6]. Forest therapy
has also been reported to improve depression [7]. Furthermore, forest therapy reportedly
reduces sympathetic nervous activity, increases parasympathetic nervous activity, and
regulates the balance of autonomic nerves, all of which lead to increased relaxation [8].
Along with its ability to reduce stress, forest therapy has been shown to improve
immune function [9,10]. Stress conditions affect immune function [11,12]. In particular,
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168440
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
2 of 17
chronic stress suppresses immune responses and promotes pathological immune responses,
including inflammatory responses [13–15]. Thus, if forest therapy can reduce stress, it will
simultaneously enhance immune function. Moreover, some studies [16,17] have reported
that environmental factors have a greater impact on immune function than genetic factors.
This indicates that environmental characteristics, such as those provided by forest therapy,
can have a positive effect on immune function.
However, although studies of forest therapy have used various outcome measures
related to immune function [18–22], such as NK cells, T cells, B cells, perforin, granulysin,
granzymes, and interleukin-6, their results show inconsistently. Therefore, it is necessary to
identify the effective measures among the various outcome measures of immune function
and to analyze which outcomes of the immune function measurements show changes due
to the intervention of forest therapy.
In addition, several researchers have presented a systematic review of studies on the
health effects of forest therapy [4,5,14,23], but few have presented a systematic review on
the effect of forest therapy on immune function specifically. Thus we present a system-
atic review of studies on the effects of forest therapy on the immune function of adults,
investigating the characteristics of forest therapy programs and analyzing their effects on
immune function measures.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Selection of Existing Studies
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting
Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [24]. The publication year of
the article was not limited. Key items of the criteria for selecting existing studies for this
study, were composed according to PICO-SD (participants, intervention, comparisons,
outcomes, and study design): (1) The participants were adults aged over 18 years; (2) The
intervention included forest therapy; (3) That the studies compared forest therapy groups,
with groups that did not participate in forest therapy intervention or urban groups, and
cases without control groups were also included; (4) Outcomes of the intervention included
immunological outcome measures, and (5) In terms of study design, all experimental
studies, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), non-equivalent control group designs
(Non-RCTs), and one-group pretest-posttest design were included. Studies without ex-
perimental designs, such as survey research and qualitative research, were excluded from
the analysis.
2.2. Searching for and Selecting Existing Studies
We included studies that could be retrieved in each database in our analysis following
a search conducted in the two weeks between 1 July and 14 July 2020. For domestic
databases, RISS, KISS, DBPia, and NDSL were used, and for international databases,
PubMed, Cochrane library, PsychoInFO, EMBASE, EBSCO, Web of Science, CINAHL,
and Scopus were used. The references of the searched articles were used to perform a
manual search in addition to the electronic search for collection. The search keywords
were (“shinrin-yoku” OR “forest bathing” OR “nature therapy” OR “forest therapy”)
AND (“Immunity” OR “Natural killer cell” OR “NK cell” OR “immune”). For domestic
keywords, Korean was used with the same meaning as the English keywords. Only studies
published in English or Korean were included.
Each database was searched following a discussion between the two researchers, and
one of the researchers deleted duplicate articles using a document management program.
The title and abstract were then reviewed according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria,
to screen the articles. Once an article passed the initial screening stage, its full text was
checked, and only those that met each of the selection criteria were selected. In the case of
any disagreement during this process, the two researchers had a discussion and reached a
mutual consensus regarding the final selection of each article.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
3 of 17
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment of Individual Studies
To assess the selected articles’ risk of bias, we used the Revised Cochrane Risk-of-Bias
tool (RoB 2) [25] for RCTs, while the Risk-of-Bias Assessment tool for Non-randomized
Study (RoBANS) [26] tool was used for Non-RCTs.
The risk-of-bias assessment tool for RCTs is composed of the following five domains:
randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data,
measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported result. The risk of bias assess-
ment for these domains was performed using three categories: “low risk”, “some concerns”,
and “high risk”.
The RoBANS is composed of the following six items: selection of participants, con-
founding variables, measurement of intervention (exposure), blinding for outcome assess-
ment, incomplete outcome data, and selective outcome reporting. The risk was assessed
using “low risk”, “high risk”, and “uncertain risk” categories. “uncertain risk” means that
the study is judged to raise some concerns in at least one domain, but not to be at high
risk of bias for any domain. In this study, two researchers independently performed a
quality evaluation. When there was a disagreement between the two researchers, included
a third-party researcher in their discussion to help bring them to an agreeable conclusion.
2.4. Data Extraction
Items for data extraction included study information (author, publication year), partici-
pants (total number of participants, age, and diagnosis), study design and intervention program
characteristics, measurement tools, main outcome variables, and ethical considerations.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
We retrieved 870 articles from domestic databases and 1972 articles from international
databases for our analysis. Once duplicate articles were removed, 1782 articles remained.
The titles and abstracts of each of these articles were reviewed, and 1718 articles did not
comply with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Finally, 64 articles remained after the
screening process. The full text of each of these articles was reviewed, and the following
50 articles were excluded in total: 40 articles that contained no report on immunological
outcomes, one article with non-experimental study, four articles that were not published in
English or Korean, four articles whose original version could not be retrieved, one article
with inadequate comparison, and one article on indirect forest therapy (aromatherapy).
Thus, only 13 peer-reviewed articles were selected for further analysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1. PRISMA flow chart.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
4 of 17
3.2. Characteristics of the Existing Studies
In terms of the selected existing studies’ publication year, there were no reports
published before 2006, while there were three articles published between 2007 and
2010 [18–20], four articles between 2011 and 2015 [21,22,27,28], and six articles from 2016 to
present [29–34]. With regard to participants, six of the studies used healthy adults as
participants [18–21,27,34], while five had participants who were adults with health prob-
lems [22,28–31], and two did not report as to their participants’ health status [32,33]. In
terms of countries/regions where the study was conducted, four studies were conducted in
Korea [27,28,30,32], China [21,29,31,34], and Japan [18–20,22], respectively, and one study
was conducted in Taiwan [33]. As for the study design, three studies were RCTs [21,29,31],
five studies used non-equivalent control group pre-posttest design [20,27,30,32,34], and
five studies used a one-group pretest-posttest design [18,19,22,28,33]. In terms of sample
size, there were seven studies with a sample size of 20 or less [18,19,21,28,29,32,33], four
studies with a sample size between 21 and 50 [20,22,27,31], and two studies with a sample
size of 51 or larger [30,34]. With regard to ethical considerations, apart from one study with
no description of Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval status [32], the other 12 studies
were all approved by the IRB (Table 1).
Table 1. General characteristics of included studies (n = 13).
Characteristic
Publication year
Participants
Country/Regions
Study Design
Sample size
Statement of ethical consideration
Categories
≤2006
2007–2010
2011–2015
≥2016
Healthy adults
Adults with health problems
Not reported
China
Korea
Japan
Taiwan
Randomized control group
Nonequivalent control group
pre-posttest design
One group pre-post test
design
≤20
21–50
≥51
Yes
No
N (%)
0 (0)
3 (23.1)
4 (30.8)
6 (46.2)
6 (46.2)
5 (38.5)
2 (15.4)
4 (30.8)
4 (30.8)
4 (30.8)
1 (7.7)
3 (23.1)
5 (38.5)
5 (38.5)
7 (53.8)
4 (30.8)
2 (15.4)
12 (92.3)
1 (7.7)

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
5 of 17
3.3. Characteristics of the Forest Therapy Program
We found that “forest bathing” was the most commonly used term in five articles,
followed by “forest therapy”, used in four articles, while “visiting forest”, “green space”,
“forest environment”, and “forest walking” were each used in one article, respectively.
The forest therapy programs were classified into lodging-type and session-type pro-
grams. For lodging-type programs, seven studies lasted for 2–3 days [18–21,27,30,34], three
studies that lasted 4–5 days [29,31,33], and one study [28] that lasted for 14 days. For
session-type programs, two studies were conducted for 12 weeks [22,32], one of which held
a session weekly [22] while the other held sessions three times weekly [32]. There were eight
studies in which the intervention only included walking in the forest [18–21,29,31–33], while
four studies used meditation, horticultural therapy, yoga meditation, support group ther-
apy, music, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and relaxation therapy as interventions, alongside
walking in the forest [22,27,28,30]. One study [34] provided no specific description of the
intervention but simply mentioned forest exposure.
There were eight studies in which the participants were healthy adults and five
studies in which the participants were adults with health problems. The healthy adult
participants included college students [19,21,34], middle-aged women or men [18,33,34],
nurses [19], and workers in the healthcare and counseling service industries [27]. As
for the participants who were adults with health problems, two studies included cancer
patients [22,28], one included patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [29],
one included chronic pain patients [30], and one study’s participants were patients with
congestive heart failure [31] (Table 2).

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
6 of 17
Authors
(Years)
1
Li et al.
(2007) [18]
2
Li et al.
(2008) [19]
3
Li et al.
(2008) [20]
Table 2. Summary of studies included in the systematic review (k = 13).
Study Design
Participants (n)
One group pre-posttest
design
Healthy male, aged
37~55 years (12)
Mean age: 43.1 ± 6.1
One group pre-posttest
design
Healthy female nurses,
aged 25~43 years (13)
Mean age: 28.8 ± 4.6
None-equivalent control
group pre-posttest
design
Healthy male, aged
35~56 years (E:12, C:11)
Mean age: 45.1 ± 6.7
Intervention
Control
Outcome (Measurements)
A three-day/two-night trip
First day: walked for two hours in the
afternoon in a forest field
Second day: walked for two hours
each in the morning and afternoon in
two different forest field
On day 3: finished the trip
A three-day/two-night trip
First day: walked for two hours in the
afternoon in a forest field
Second day: walked for two hours
each in the morning and afternoon in
two different forest field
On day 3: finished the trip
A three-day/two-night forest bathing
program
First day: walked for two hours in the
afternoon in a forest field
Second day: walked for two hours
each in the morning and afternoon in
two different forest field
On day 3: finished the trip
None
None
A three-day/two-night
city trip
First day: walked for two
hours in the afternoon in
an old-style district in the
city
Second day: walked for
two hours around baseball
Dome in the morning and
2 h around/in airport in
the afternoon
On day 3: finished the trip
· NK cells **↑, NK activity **↑,
· T cells
· granulysin **↑, perforin **↑,
granzymes A **↑/B **↑
· WBC, (Lymphocytes *↑,
Monocytes*↑,
Granulocytes **↓)
· T-A *↓, D *↓, A-H, F, C, V **↑(POMS)
· the hours of sleep
· NK cells **↑, NK activity **↑
· T cells *↓
· granulysin **↑, perforin **↑,
granzymes A **↑/B **↑
· Adrenalin **↓, noradrenaline (Urine)
**↓
· Estradiol, progesterone
· T-A, D **↓, A-H, F, C, V (POMS)
· NK cells *↑, NK activity *↑
· T cells
· granulysin **↑, perforin **↑,
and granzymes A **↑/B **↑
· WBC
· Adrenaline (Urine) *↓

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
7 of 17
Authors
(Years)
4
Mao et al.
(2012) [21]
5
Nakau et al.
(2013) [22]
6
Jung et al.
(2015) [27]
7
Kim et al.
(2015) [28]
Table 2. Cont.
Study Design
Participants (n)
Intervention
Control
Outcome (Measurements)
RCT
One group pre-posttest
design
None-equivalent control
group pre-posttest
design
One group pre-posttest
design
Healthy male university
students
(E:10, C:10)
Mean age: 20.79 ± 0.54
Breast cancer or lung
cancer (22)
Mean age: 58.1 ± 10.8
Workers in the
healthcare and
counseling service
industries (E:19, C:20)
Mean age
E: 29.42 ± 8.92,
C:36.45 ± 12.23
Stage 3 Breast cancer
patient, aged 25~60
years (11)
Mean age: 56 ± 5.12 (11)
two-night trip
walked for 1.5 h each in the morning
and afternoon in a forest field
Walking in the forest, Horticultural
therapy, yoga meditation, and
support group therapy, and sessions
were conducted once a week for 12
weeks
3 days, 2 nights, Walking and
meditation in the forest, and exposure
to a psychological program using
music and cognitive-behavioral
therapy.
Stay in the forest for 14 days, Forest
therapy program (Walk, forest life)
walked for 1.5 h each in
the morning and afternoon
in a city site
None
frequently use the
environment without
participating in the
program
None
· NK cells
· T cell, B cell *↑, T-helper cells.
suppressor cells, natural killer cells
· IL-6*↓, TNF-α *↓
· T-SOD, MDA **↓
· ET-1 **↓, Platelet activation
· Cortisol *↓, Testosterone
· T-A *↓, D *↓, A-H *↓, F *↓, C, V
*↑(POMS)
· NK activity **↑
· Well-being of functional and
spiritual (FACIT-Sp): GP, GS, GE, GF
*↑, Sp *↑
· Quality of life (SF-36): PF *↑, RP *↑,
BP,
GH *↑, VT **↑, SF, RE *↑, MH *↑
· Fatigue (CFS) **↓
· T-A *↓, D, A-H, F, C **↓, V (POMS)
· STAI: State anxiety **↓, Trait anxiety
*↓
· NK activity
· Cortisol *↑
· HRV
· MBI-GS **↓, WRSI *↓, REQ **↑
· NK cells **↑
· Perforin *↑, Granzyme B *↑

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
8 of 17
Authors
(Years)
8
Jia et al.
(2016) [29]
9
Han et al.
(2016) [30]
10
Mao et al.
(2017) [31]
11
Lee et al.
(2017) [32]
Table 2. Cont.
Study Design
Participants (n)
Intervention
Control
Outcome (Measurements)
RCT
None-equivalent control
group pre-posttest
design
RCT
None-equivalent control
group pre-posttest
design
elderly patients
with chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (E:
10, C: 8)
Mean age
E: 70.1 C: 70
Full-time employees
with chronic widespread
pain for more than three
months, aged 25~49
years
(E: 33, C: 28)
Mean age
E: 41.6 ± 6.5, C:
37.5 ± 8.4
Elderly patients with
chronic heart failure,
Aged from 65 to 80 years
(E: 23, C: 10)
Mean age
73.86 ± 5.85 years old
Women in their 50 s (E: 9,
C: 9)
Mean age
E: 53.9 ± 2.69, C:
55.5 ± 1.84
4 days, walking in the forest (total 3 h
walk/day)
2 days forest therapy program
Walking and therapeutic activities in
the forest activities (music therapy,
psycho-education: coping with pain
and stress, bodily exercises,
mindfulness-based meditation)
4 days, Walking in the forest (total 3 h
walk/day)
Forest walking exercise for 12 weeks
(3 times/week, 110 min/day)
4 days, walking in the city
(total 3 h walk/day)
The control group was
instructed not to conduct
either heavy loads of
domestic or occupational
work during the
enrollment in this study.
4 days, Walking in the city
(total 3 h walk/day)
Ground walking exercise
for 12 weeks (3
times/week, 110 min/day)
· NK cells, NKT-like cell, CD8+ T cells
· Perforin **↓, Granzyme B
· IL-6 *↓, IL-8 **↓, interleukin-1β *↓,
TNF-α
interferon-γ *↓, CRP *↓
· Cortisol *↓, Epinephrine *↓
· RARC/CCL-18 **↓, TIMP-1 *↓, SP-D
*↓
· T-A **↓, D *↓, A-H *↓, F, C, V
(POMS)
· NK activity **↑
· Heart rate variability (HRV) **↑
· Self-reported pain **↓ (VAS)
· Depression **↓ (BDI)
· Health-related quality of life **↑
(EQ-VAS)
· IL-6 *↓, TNF-α, CRP
· BNP **↓, N-terminal pro BNP
· ET-1 **↓, Renin, AGT, Ang II, AT1,
AT2 **↑
· T-SOD *↑, MDA *↓
· T-A *↓, D **↓, A-H **↓, F, C **↓, V
(POMS)
· NK cells *↑
· Melatonin *↑

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
9 of 17
Table 2. Cont.
Authors
(Years)
Study Design
Participants (n)
Intervention
Control
Outcome (Measurements)
12
Tsao et al.
(2018) [33]
One group pre-post test
design
Middle-aged subjects
(11)
Mean age: 60.4
A five-day/four-night trip (maintain
dietary control and walking exercise)
First day: walked for 1.5 h in the
afternoon in a forest field
Next three days: walked for 1.5 h
each in the morning and afternoon in
two different forest field
Fifth day: finished the trip
None
· NK cells, NK activity **↑
13
Lyu et al.
(2019) [34]
None-equivalent control
group pre-posttest
design
Male College Students
(E: 45, C: 15)
Mean age
E: 20.9 ± 0.24, C:
21.3 ± 0.45
Bamboo forest site exposure for three
days
City site exposure for three
days
· NK cells *↑. NK activity *↑,
· granulysin, perforin *↑,
granzymes A *↑/B *↑,
· corticosterone *↓
· SBP *↓, DBP, HR, SpO2
· T-A *↓, D *↓, A-H *↓, F *↓, C *↓, V *↑
(POMS)
*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ↑: indicators rise; ↓: indicators decline; E = Experimental group; C = Control group; POMS = Profile of mood states; T-A = Tension-anxiety; D = Depression: A-H = Anger-hostility,; F = fatigue;
C = Confusion; V = Vigor; WBC = hite blood cell; IL-6 = Interleukin-6; TNF-α = Tumor necrosis factors α; T-SOD = Total superoxide dismutase; MDA = Activity and malondialdehyde; ET-1 = Endothelin-1;
FACIT-Sp = Functional assessment of chronic illness therapy-spiritual; GP = Physical well-being; GS = Social/family well-being; GE = Emotional well-being; GF = Functional well-being; Sp = Spiritual well-being;
CFS = Cancer fatigue scale; SF-36 = 36-Item short-form health survey; PF = Physical functioning; RP = Role-physica; BP = Bodily pain; GH = General health perception; VT = Vitality; SF = social functioning;
RE = Role emotional; MH = Mental health; STAI = State-trait anxiety inventory; HRV = Heart rate variability; MBI-GS = Maslach Burnout Inventory-General Survey; WRSI = Worker’s Stress Response Inventory;
REQ = Recovery Experience Questionnaire; CRP = C-peptide protein; RARC/CCL-18= Pulmonary and activation-regulated chemokine, TIMP-1= Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1; SP-D = Surfactant
protein D; VAS: Visual analog scale; BDI = Beck Depression Inventory; EQ-VAS= EuroQol Visual Analog Scale; BNP = Brain natriureti; AGT = Angiotensinogen; Ang II = Angiotensin II; AT1 = Angiotensin II type
1 receptor; AT2 = Angiotensin II type 2 receptor; SBP = Systolic blood pressure; DBP = Diastolic blood pressure; HR = Heart rate.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
10 of 17
3.4. Effects of Forest Therapy on Immune Function
With regard to immune function measures, the number of NK cells or NK cell activity
was the most frequent measure used in the studies we reviewed. The number of NK cells
was reported in nine studies [18–21,28,29,32–34]; a significant increase in NK cell count
was reported in six studies [18–20,28,32,34], and no significant change in the number of
NK cells was reported in three studies [21,29,33].
NK cell activity was measured in eight studies [18–20,22,27,30,33,34], and a significant
change was reported in seven studies. The study that reported no significant change in
the activity of NK cells [27] applied a combination of interventions, including walking,
meditation, counseling, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and music therapy for three days
and two nights in the forest, for workers in the healthcare and counseling service industries.
In a study with female nurses as participants, which used a walking intervention of two
hours in the morning and afternoon, respectively, for three days and two nights [19], a
significant increase in both the number and activity of NK cells was reported, for up to
7 days after returning from the forest. In addition, in a study with healthy male adults as
participants which used a walking intervention of two hours each morning and afternoon,
respectively, for three days and two nights [20], a significant increase in the number and
activity of NK cells was reported for not only up to 7 days after the intervention, but also
30 days after returning from the forest.
T cells were measured in four studies [18–21] and showed no significant changes
in three of these studies [18,20,21]. In a study with healthy male university students
as participants, where the intervention included 90 min of walking in the morning and
afternoon, respectively, for two days [21], B cells, T-helper cells, suppressor cells, and NK
cells were measured; a significant change was observed only in B cells. In a study in which
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease participated, that included 90 min
of walking intervention in the morning and afternoon, respectively, for four days [29], no
significant changes were seen in the Natural Killer T(NKT)-like cells or CD8+ T cells.
Six studies [18–20,28,29,34] measured granulysin, perforin, and granzymes A and B,
which are cytotoxic effector molecules. In a study with male college students as partici-
pants [34], there was no significant change in granulysin, and in a study with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease patients as participants [29], there was no significant
change in granzyme B, while significant changes in these measures were reported in four
other studies.
Three studies [21,29,31] measured the levels of proinflammatory cytokines. In a study
that used a walking intervention for healthy male university students [21], IL-6 and TNF-α
were measured, and significant changes were reported in both. In a study that used 90 min
of walking intervention for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, in the
morning and afternoon, respectively, for four days in the forest [29], IL-6, IL-8, IFN-γ, IL-1β,
and TNF-α were measured; significant changes were reported in each of these outcome
measures apart from TNF-α. In a study that used a walking intervention for chronic heart
failure patients for four days in the forest [31], there was a significant change seen in IL-6
levels, but no significant change was reported in TNF-α levels (Table 3).
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
11 of 17
Table 3. Summary of the effects of forest therapy on immune function.
Outcome
Number of NK cells
NK cells cytotoxic activity
T cells
B cells
T suppressor cells
T-helper cells
Natural killer T(NKT) like cells
Cytotoxic T cells
Cytotoxic effector
molecules
granulysin
perforin
granzymes A
granzymes B
Proinflammatory
cytokines
interleukin-6 (IL-6)
interleukin-8 (IL-8)
interferon-γ (IFN-γ)
interleukin-1β (IL-1β)
tumor necrosis factor α
(TNF-α)
Article Number
Significant
Not Significant
18, 19, 20, 28, 32, 34
18, 19, 20, 22, 30, 33, 34
19
21
21, 29, 33
27
18, 20, 21
21
21
29
29
18, 19, 20
34
18, 19, 20, 28, 29, 34
18, 19, 20, 34
18, 19, 20, 28. 34
29
21, 29, 31
29
29
29
21
29, 31
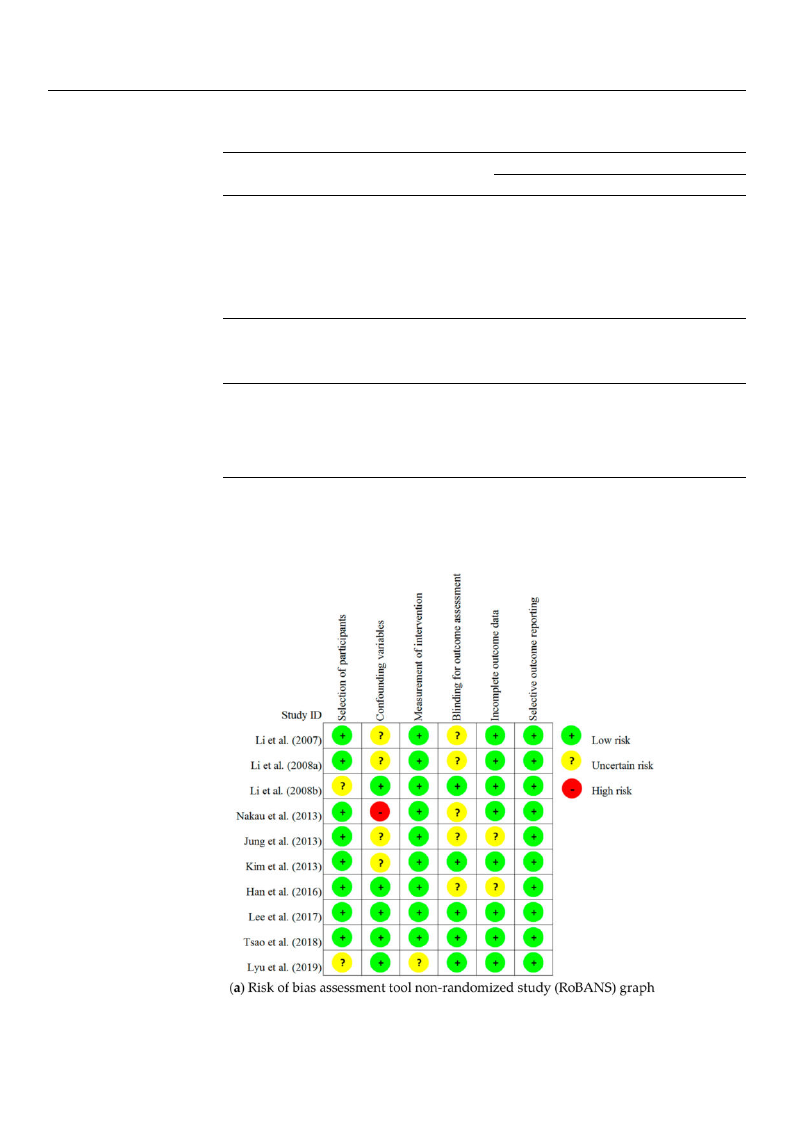
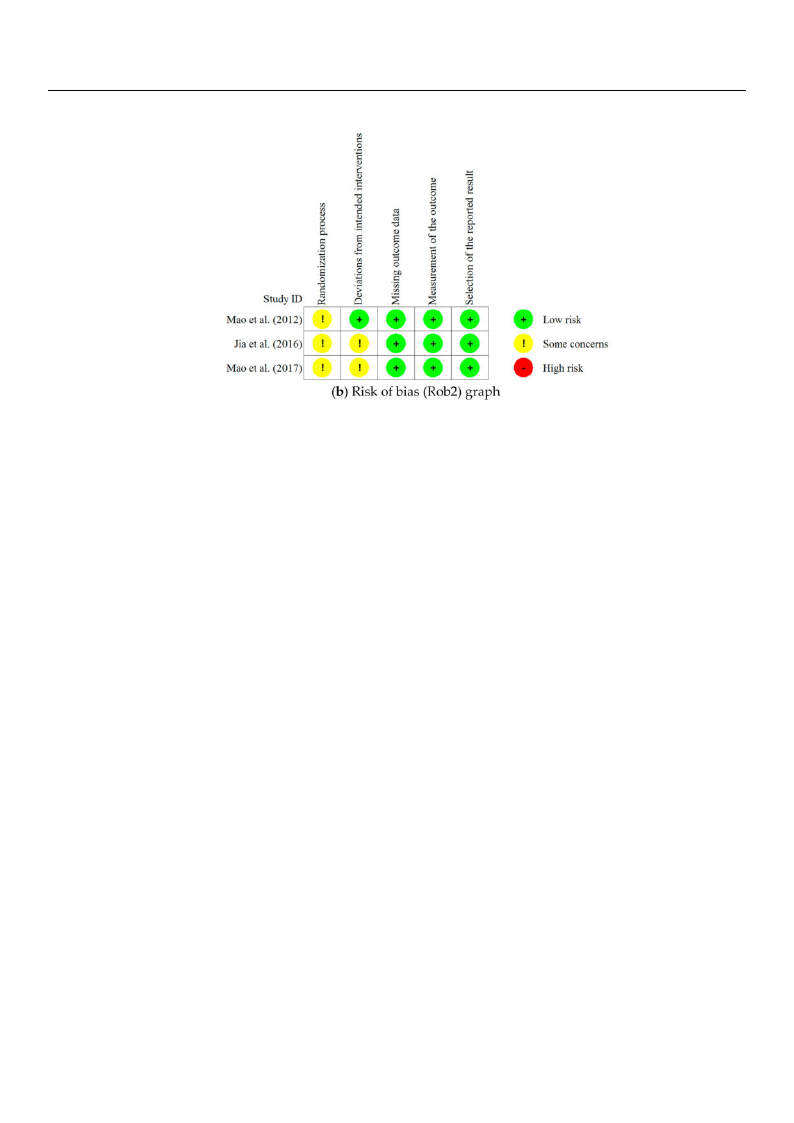
3.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
The results of the risk of bias assessment we conducted on the 13 articles reviewed in
this study are presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Cont.
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
12 of 17
Figure 2. Risk of bias in included studies.
With regard to the three RCTs, none of the three articles included a detailed description
of the randomization process and thus were assessed as having “some concerns” in the
category of Randomization Process. In terms of Deviations from Intended Interventions, no
information on dropouts was presented and the dropouts were not included in the analysis
of two of the RCTs; thus, these two studies were assessed as having “some concerns,”
while the other RCT was assessed as “low risk.” In terms of Missing Outcome Data,
Measurement of the Outcome, and Selective Outcome Reporting, all three studies were
assessed as “low risk.”
Of the 10 non-RCT studies, two were assessed as of “uncertain risk” because the
recruitment criteria of the patient group and control group were not consistent in terms of
Selection of Participants, and the rest were assessed as “low risk.” In terms of Confounding
Variables, one study was assessed as “high risk”, because there was no clear description
of the management of NK cells, and multiple items of subjective quality assessment
were related to the intervention and determined as the factors affecting the outcomes.
Further, four studies were assessed as being of “uncertain risk” because they gave no clear
description of the control of variables nor any clear information on the exclusion of the
time elapsed, considering the intervention. The remaining studies were assessed as “low
risk.” In terms of Measurement of Intervention (Exposure), one study was assessed as
being of “uncertain risk” because it did not give a sufficiently detailed description of the
intervention (exposure) method other than naming the place of intervention, while the
other nine studies were assessed as “low risk.”
In terms of the Blinding for Outcome Assessment, five studies were assessed as being
of “uncertain risk” because it was unclear whether the blinding status would affect outcome
measurements, while the other studies were assessed as “low risk.” In terms of Incomplete
Outcome Data, two studies were assessed as being of “uncertain risk”, because they did
not have sufficient information on missing data, and the other studies were assessed as
“low risk.” In terms of Selective Outcome Reporting, all 10 studies included all expected
outcomes, and they were assessed as “low risk”.
4. Discussion
This systematic review of studies on the effects of forest therapy on immune function
aims to identify the characteristics of forest therapy programs and to analyze the effects of
forest therapy on immune function outcome measures.
Since 2006, all studies have investigated the effects of forest therapy on immune
function. An increasing number of studies have been conducted within the last five years,
indicating a recent surge of interest in the effects of forest therapy on immune function.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
13 of 17
However, among the studies published so far, one group of pre-post test design studies
accounted for a high proportion (38.5%), and the sample size of each of the studies we
reviewed was small. This indicates that a low level of evidence is provided by these studies.
In order to produce more systematic and scientific results, a more stringently controlled
study design will be required in future research.
Examining the details of the forest programs reveals that 61.5% of the studies only used
a forest walking intervention and no other interventions. In fact, the majority of studies
used a walking intervention, meaning that the main component of forest therapy was
walking. This finding is consistent with the results of a previous forest therapy study [35],
in which walking accounted for a major part of the forest therapy program’s composition.
In terms of the intervention period, programs were classified into lodging-type (lasting
anywhere from three days and two nights to 14 days) and session-type programs. No
program operated as a short-term one-off type, as reported by Chae et al. [6], indicating
that an intervention period of a minimum of two nights and three days is required for the
improvement of immune function and maintenance of improved outcomes.
To date, there have been few standardized forest therapy programs and insufficient
individual forest therapy studies, posing difficulties in clearly identifying the most effective
intervention method [36]. Only 13 articles were included in this systematic review and
the studies presented were highly heterogeneous and thus unsuitable for meta-analysis.
Consequently, we were only able to conduct a systematic review of these existing studies.
If more individual studies are accumulated in the future, we will perform a meta-analysis
according to intervention type and duration, which will enable a more objective evaluation
of the effects of forest therapy on immune function.
We considered the number of NK cells, NK activity, and cytotoxic effector molecules
as measures to evaluate forest therapy’s effects on immune function. In 12 of the reviewed
studies, the number of NK cells and/or NK activity was reported. NK cells are capable
of attacking and killing virus-infected cells or tumor cells and play an important role in
the human endocrine and immune systems [37]. It is thought that NK cells were often
measured in these studies because, in the forest environment, the activity of NK cells
is enhanced by an increase in the number of NK cells and cytotoxic effector molecules,
leading to enhanced immune function [18,38]. In general, NK cells are highly important
lymphocytes [39] that serve as a first-line defense against virus-infected cells. They rapidly
proliferate in the stress of transient acute exercise but are vulnerable to chronic stress.
Among the lymphocyte subtypes (T cells, B cells, and NK cells), NK cells are known to be
most responsive to exercise intensity [40].
In this study, six of the nine studies that reported the number of NK cells reported a
significant increase in the number following forest therapy intervention, and out of the eight
studies that reported the activity of NK cells, seven reported a significant increase in NK
cell activity following forest therapy intervention. In particular, two studies with healthy
adults [19,20] revealed that the number and activity of NK cells continued to increase
significantly, for up to seven days or longer after returning to the urban environment, while
a study [20] with healthy male adults showed a significant increase in NK cell activity up
to 30 days after the intervention. In other words, the results indicate that forest therapy can
have a long-term effect on the number and activity of NK cells in the human body. The
study [28] on an urban woman with breast cancer who had received anti-cancer treatment
suggested the potential of forest therapy as adjuvant anti-cancer therapy after standard
treatments. However, since both healthy adults and adults with health problems were
included in the studies that showed a significant change and the studies that did not
show a significant change, and because the type of forest therapy was different in different
studies, our investigation of the difference in the effects according to the characteristics of
participants and the types of forest therapy programs was limited.
Of the seven studies that analyzed cytotoxic effector molecules such as perforin,
the majority reported significant changes in the outcomes. This could be because NK
cells secrete perforin and granzymes [41,42], and granulysin [43,44] through the granule

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
14 of 17
exocytosis pathway, which leads to the destruction of tumor cells or virus-infected cells.
Activation of NK cells via the release of perforin and granzymes is important for inducing
natural cytotoxicity [45]. Studies in perforin-deficient mice indicated that NK cell-mediated
cytotoxicity is greatly impaired in such mice [46]. The NK cells of mice with a deficiency in
the granzyme B cluster, induce apoptosis in target cells more slowly than wild-type NK
cells [47].
A number of studies [1,7,8,38,48,49] reported that volatile substances (phytoncides)
extracted from trees have a positive effect on immune function, supporting the idea that a
forest’s environmental factors play an instrumental role in improving immune function.
An in vitro study indicated that certain volatile tree chemicals, called phytoncides, increase
the activation of NK cells and intracellular anti-cancer molecules [50]. This assertion is
supported by several studies in animals [51,52] and humans [53], suggesting that fragrances
from trees can reverse stress-induced immunosuppression, and normalize immune function
and neuroendocrine hormone levels.
Stress increases sympathetic nervous system activity and hypothalamus-pituitary-
adrenal system activity to increase cortisol secretion. However, phytoncides have positive
effects on stress reduction, cortisol level reduction, blood pressure reduction, immune sys-
tem enhancement, autonomic nervous system, and chronic fatigue, without side effects [54].
It has also been reported that inhalation of phytoncide through breathing during forest
bathing, or smell, can enhance the cytotoxic activity of NK cells [55]. In addition, NK cells
are increased by the decreased production of stress hormones and the increased production
of anticancer proteins caused by phytoncides [49].
Several studies have analyzed cytokines such as interferon-γ, interleukin-1β, and
tumor necrosis factor α or lymphocyte subtypes, but it was difficult to determine outcomes
from their results due to their small number. However, in the case of T cells, previous re-
search suggests that careful consideration is required while selecting T cells for verification
of forest therapy effects in the future, as three out of four studies included in this review
reported that there were no significant changes in T cells.
One limitation of this study is that it analyzed only articles written in English and
Korean, and included non-RCT studies as well as RCT studies that have a high level
of evidence. In addition, since only a small number of studies were included, another
limitation was found in presenting the effect size according to the characteristics of the
participants or the program used. However, this systematic review is significant in that it
suggests that there is evidence to support the theory that forest therapy can have a positive
effect on immune function.
5. Conclusions
The results of this review recommend the use of the number or activity of NK cells
for evaluating the effects of forest therapy on immune function, and cytotoxic effector
molecules are also thought to serve as effective outcome measures. Forest therapy pro-
grams, including walking in the forest, may contribute to the improvement of immune
function, and forest therapy is expected to be utilized for the enhancement of immune
function in the future.
More RCT studies on the effects of forest therapy on immune function are necessary,
to strengthen the body of evidence to support the use of forest therapy for improving
immune function.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, Y.C. and S.L.; methodology, Y.C. and S.L.; software, S.L.,
S.P. and H.K.; validation, Y.C., S.L., Y.J., S.K., S.P. and H.K.; formal analysis, S.L.; investigation, Y.C.,
S.L., Y.J., S.K., S.P. and H.K.; data curation, S.L. and S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.;
writing—review and editing, Y.C.; visualization, S.L.; supervision, Y.C.; project administration, Y.C.;
funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant
funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2019R1F1A1060253).

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
15 of 17
Institutional Review Board Statement: Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement: No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is
not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
1. Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of nature therapy: A review of the research in japan. Int. J. Environ. Res.
Public Health 2016, 13, 781. [CrossRef]
2. Park, J.S.; Yeon, P.S. A network analysis on the forest healing issues using big data—Focused on Korean web news from 2005 to
2019. J. KIFR 2020, 24, 63–71.
3. Lee, D.G.; Jeong, Y.M.; Lee, M.M.; Shin, W.S.; Yoon, Y.K. The effect of socio-psychological stress on mental well-being mediated by
perceived restorativeness-Focusing on visitors whose motive for visiting the forest is ‘COVID-19’. J. KIFR 2020, 24, 99–108.
4. Lee, I.; Choi, H.; Bang, K.-S.; Kim, S.; Song, M.; Lee, B. Effects of Forest Therapy on Depressive Symptoms among Adults: A
Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 321. [CrossRef]
5. Oh, B.; Lee, K.J.; Zaslawski, C.; Yeung, A.; Rosenthal, D.; Larkey, L.; Back, M. Health and well-being benefits of spending time in
forests: Systematic review. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2017, 22, 71. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
6. Chae, Y.R.; Lee, S.H. Systematic review of forest therapy program for adult patients with diseases. J. Korean Biol. Nurs. Sci. 2020,
22, 157–171. [CrossRef]
7. Woo, J.M.; Park, S.M.; Lim, S.K.; Kim, W. Synergic effect of forest environment and therapeutic program for the treatment of
depression. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2012, 101, 677–685.
8. Li, Q.; Kawada, T. Effect of forest therapy on the human psycho-neuro-endocrino- immune network. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 2011,
66, 645–650. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
9. Lee, B.K.; Lee, H.H. A Study on the effects of human physiology after forest phytoncide therapy. J. Naturopath. 2012, 1, 14–20.
10. Song, J.H.; Cha, J.G.; Lee, C.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Yeon, P.S. Effects of forest healing program on stress response and spirituality in female
nursing college students and there experience. J. KIFR 2014, 18, 109–125.
11. Steptoe, A.; Hamer, M.; Chida, Y. The effects of acute psychological stress on circulating inflammatory factors in humans: A
review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 901–912. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
12. Segerstrom, S.C.; Miller, G.E. Phychological stress and the human immune system: A meta-analytic study of 30 years of inquiry.
Psychol. Bull. 2004, 130, 601–630. [CrossRef]
13. Dhabhar, F.S. Effects of stress on immune function: The good, the bad, and the beautiful. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 193–210.
[CrossRef]
14. Walburn, J.; Vedhara, K.; Hankins, M.; Rixon, L.; Weinman, J. Psychological stress and wound healing in humans: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 2009, 67, 253–271. [CrossRef]
15. Webster Marketon, J.I.; Glaser, R. Stress hormones and immune function. Cell. Immunol. 2008, 252, 16–26. [CrossRef]
16. Roederer, M.; Quaye, L.; Mangino, M.; Beddall, M.H.; Mahnke, Y.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Tosi, I.; Napolitano, L.; Terranova, B.M.;
Menni, C.; et al. The genetic architecture of the human immune system: A bioresource for autoimmunity and disease pathogenesis.
Cell 2015, 161, 387–403. [CrossRef]
17. Brodin, P.; Jojic, V.; Gao, T.; Bhattacharya, S.; Angel, C.J.; Furman, D.; Shen-Orr, S.; Dekker, C.L.; Swan, G.E.; Butte, A.J.; et al.
Variation in the human immune system is largely driven by non-heritable influences. Cell 2015, 160, 37–47. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
18. Li, Q.; Morimoto, K.; Nakadai, A.; Inagaki, H.; Katsumata, M.; Shimizu, T.; Hirata, Y.; Hirata, K.; Suzuki, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; et al.
Forest bathing enhances human natural killer activity and expression of anti-cancer proteins. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol.
2007, 20, 3–8. [CrossRef]
19. Li, Q.; Morimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Inagaki, H.; Katsumata, M.; Hirata, Y.; Hirata, K.; Shimizu, T.; Li, Y.J.; Wakayama, Y.; et al. A
forest bathing trip increases human natural killer activity and expression of anti-cancer proteins in female subjects. J. Biol. Regul.
Homeost. Agents. 2008, 22, 45–55. [PubMed]
20. Li, Q.; Morimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Inagaki, H.; Katsumata, M.; Hirata, Y.; Hirata, K.; Suzuki, H.; Li, Y.J.; Wakayama, Y.; et al.
Visiting forest, but not a city, increases human natural killer activity and expression of anti-cancer proteins. Int. J. Immunopathol.
Pharmacol. 2008, 21, 117–127. [CrossRef]
21. Mao, G.X.; Lan, X.G.; Cao, Y.B.; Chen, Z.M.; He, Z.H.; Lv, Y.D.; Wang, Y.Z.; Hu, X.L.; Wang, G.F.; Yan, J. Effects of short-term forest
bathing on human health in a broad-leaved evergreen forest in Zhejiang province, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 317–324.
[PubMed]
22. Nakau, M.; Imanishi, J.; Imanishi, J.; Watanabe, S.; Imanishi, A.; Baba, T.; Hirai, K.; Ito, T.; Chiba, W.; Morimoto, Y. Spiritual care
of cancer patients by integrated medicine in urban green space: A pilot study. Explore 2013, 9, 87–90. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
23. Ideno, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Abe, Y.; Ueda, K.; Iso, H.; Noda, M.; Lee, J.; Suzuki, S. Blood pressure-lowering effect of Shinrin-yoku
(Forest bathing): A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 409. [CrossRef]
24. Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and
meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [CrossRef]

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
16 of 17
25. Sterne, J.A.C.; Savovic´, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge,
S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials. Br. Med. J. 2019, 366, l4898. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
26. Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Seo, Y.J.; Jang, B.H.; Son, H.J.; Suh, H.S.; Shin, C.M. NECA’s Guidance for Undertaking Systematic Reviews and
Meta-Analyses for Intervention; National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency: Seoul, Korea, 2011; pp. 65–78.
27. Jung, W.H.; Woo, J.M.; Ryu, J.S. Effect of a forest therapy program and the forest environment on female workers’ stress. Urban
For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 274–281. [CrossRef]
28. Kim, B.J.; Jeong, H.; Park, S.; Lee, S. Forest adjuvant anti-cancer therapy to enhance natural cytotoxicity in urban women with
breast cancer: A preliminary prospective interventional study. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2015, 7, 474–478. [CrossRef]
29. Jia, B.B.; Yang, Z.X.; Mao, G.X.; Lyu, Y.D.; Wen, X.L.; Xu, W.H.; Lyu, X.L.; Cao, Y.B.; Wang, G.F. Health effect of forest bathing trip
on elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 29, 212–218.
30. Han, J.W.; Choi, H.; Jeon, Y.H.; Yoon, C.H.; Woo, J.M.; Kim, W. The effect of forest therapy on coping with chronic widespread
pain: Physiological and psychological differences between participants in a forest therapy program and a control group. Int. J.
Environ. Res. Public Health. 2016, 13, 255. [CrossRef]
31. Mao, G.; Cao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Xing, W.; Ren, X.; Lv, X.; Dong, J.; et al. The salutary influence of forest
bathing on elderly patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2017, 14, 368. [CrossRef]
32. Lee, M.O.; Shin, C.S.; Yeon, P.S.; Shin, M.J.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.H. The effects of forest-walking exercise on NK cells and blood
melatonin levels of women in their 50s. J. KIFR. 2017, 21, 39–52.
33. Tsao, T.M.; Tsai, M.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Cheng, W.F.; Wu, C.F.; Chou, C.K.; Su, T.C. Health effects of a forest environment on natural
killer cells in humans: An observational pilot study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16501–16511. [CrossRef]
34. Lyu, B.; Zeng, C.; Xie, S.; Li, D.; Lin, W.; Li, N.; Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q. Benefits of a three-day bamboo forest therapy session
on the psychophysiology and immune system responses of male college students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 4991.
[CrossRef]
35. Lee, I.; Bang, K.S.; Kim, S.; Song, M.; Kang, K. Status of health promotion programs utilizing forest—Based on 2015–2016 regional
healthcare plans in korea. J. Naturopath. 2016, 20, 39–52.
36. Chae, Y.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, H.J. Literature review of forest healing therapy on Korean adult. J. Korean Biol. Nurs. Sci. 2018, 20,
122–131. [CrossRef]
37. Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Baratin, M.; Walzer, T.; Ugolini, S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 503–510.
[CrossRef]
38. Park, B.J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Kasetani, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. The physiological effects of Shinrin-yoku (taking in the forest
atmosphere or forest bathing): Evidence from field experiments in 24 forests across Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15,
18–26. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
39. Trinchieri, G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv. Immunol. 1989, 47, 187–376.
40. Na, J.C. Exercise Immunology; DaeKyung Book Publishing: Seoul, Korea, 2002.
41. Li, Q.; Nakadai, A.; Ishizaki, M.; Morimoto, K.; Ueda, A.; Krensky, A.M.; Kawada, T. Dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinyl phosphate
(DDVP) markedly decreases the expression of perforin, granzyme A and granulysin in human NK-92CI cell line. Toxicology 2005,
213, 107–116. [CrossRef]
42. Smyth, M.J.; Kelly, J.M.; Sutton, V.R.; Davis, J.E.; Browne, K.A.; Sayers, T.J.; Trapani, J.A. Unlocking the secrets of cytotoxic granule
proteins. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 70, 18–29. [CrossRef]
43. Okada, S.; Li, Q.; Whitin, J.C.; Clayberger, C.; Krensky, A.M. Intracellular mediators of granulysin-induced cell death. J. Immunol.
2003, 171, 2556–2562. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
44. Krensky, A.M.; Clayberger, C. Granulysin: A novel host defense molecule. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1789–1792. [CrossRef]
45. Smyth, M.J.; Cretney, E.; Kelly, J.M.; Westwood, J.A.; Street, S.E.; Yagita, H.; Takeda, K.; van Dommelen, S.L.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.;
Hayakawa, Y. Activation of NK cell cytotoxicity. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 501–510. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
46. Kägi, D.; Ledermann, B.; Bürki, K.; Seiler, P.; Odermatt, B.; Olsen, K.J.; Podack, E.R.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Hengartner, H. Cytotoxicity
mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature 1994, 369, 31–37. [CrossRef]
[PubMed]
47. Heusel, J.W.; Wesselschmidt, R.L.; Shresta, S.; Russell, J.H.; Ley, T.J. Cytotoxic lymphocytes require granzyme B for the rapid
induction of DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in allogeneic target cells. Cell 1994, 76, 977–987. [CrossRef]
48. Tsunetsugu, Y.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.J.; Miyazaki, Y. Trends in research related to “Shinrin-yoku” (taking in the forest
atmosphere or forest bathing) in Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15, 27–37. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
49. Li, Q.; Kobayashi, M.; Wakayama, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Katsumata, M.; Hirata, Y.; Hirata, K.; Shimizu, T.; Kawada, T.; Park, B.-J.; et al.
Effect of phytoncide from trees on human natural killer cell function. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 951–959. [CrossRef]
[PubMed]
50. Li, Q.; Nakadai, A.; Matsushima, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Krensky, A.M.; Kawada, T.; Morimoto, K. Phytoncides (wood essential oils)
induce human natural killer cell activity. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2006, 28, 319–333. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
51. Hochman, P.S.; Cudkowicz, G.; Dausset, J. Decline of natural killer cell activity in sublethally irradiated mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
1978, 61, 265–268. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
52. Shibata, H.; Fujiwara, R.; Iwamoto, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Yokoyama, M.M. Immunological and behavioral effects of fragrance in
mice. Int. J. Neurosci. 1991, 57, 151–159. [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8440
17 of 17
53. Komori, T.; Fujiwara, R.; Tanida, M.; Nomura, J.; Yokoyama, M.M. Effects of citrus fragrance on immune function and depressive
states. Neuroimmunomodulation 1995, 2, 174–180. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
54. Park, S.N. A Study on Anti-Stress Effect of Phytoncides. Ph.D. Thesis, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea, 2016; Unpublished.
55. Kim, H.M.; Cho, J.K.; Ahn, K.M.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, D.M.; Min, C.K. Antitumor effects of phytoncides: Vitalization of
natural killer cells. J. Sci. Educ. Gift. 2013, 5, 96–104.
