
International Journal of
Environmental Research
and Public Health
Article
The Physio-Psychological Effect of Forest Therapy Programs on
Juvenile Probationers
Jin Young Jeon 1 , In Ok Kim 1, Poung-sik Yeon 2 and Won Sop Shin 2,*
1 Department of Forest Therapy, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 28644, Korea;
forest-bb@naver.com (J.Y.J.); inoya88@hanmail.net (I.O.K.)
2 Department of Forest Sciences, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 28644, Korea;
imoscow@hanmail.net
* Correspondence: shinwon@chungbuk.ac.kr; Tel.: +82-43-261-2536
Citation: Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, I.O.; Yeon,
P.-s.; Shin, W.S. The
Physio-Psychological Effect of Forest
Therapy Programs on Juvenile
Probationers. Int. J. Environ. Res.
Public Health 2021, 18, 5467. https://
doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105467
Abstract: The study aimed to investigate the psychological and physiological effects of forest ther-
apy programs on adolescents under probation. Fifty probationary teenagers from the Ministry of
Gyeonggi Justice Compliance Support Center participated in the study. The study explored the
effectiveness of a nonrandomized control group pretest–posttest design forest therapy program. The
forest therapy program was conducted for two days and one night for the experimental groups
(N = 33), who participated in the forest therapy program, and the control group (N = 17), who re-
ceived two days of attendance center orders program in the lecture room of the Ministry of Gyeonggi
Justice Compliance Support Center. As a result, adolescents under probation who participated
in forest therapy programs had a beneficial effect on psychological well-being (K-WBMMS) and
HRV’s HF (high frequency) and LF/HF (A ratio of Low Frequency to High Frequency) compared to
those who received the general attendance center orders program. These results support that forest
therapy programs play a positive role in the psychological and physiological effects of probationary
adolescents and can affect the diversity of rehabilitation programs for probationary adolescents.
Keywords: juvenile delinquents; adolescents; forest therapy; anti-recidivism programs; psychological
well-being; HRV
Academic Editors: Matt DeLisi and
Po-See Chen
Received: 18 December 2020
Accepted: 11 May 2021
Published: 20 May 2021
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral
with regard to jurisdictional claims in
published maps and institutional affil-
iations.
Copyright: © 2021 by the authors.
Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
This article is an open access article
distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons
Attribution (CC BY) license (https://
creativecommons.org/licenses/by/
4.0/).
1. Introduction
Delinquency, which was previously limited to unsupervised wandering, has emerged
as a serious social problem as the proportion of violent crimes such as theft, school vio-
lence, group sexual assault, and murder has increased daily. Since 1989, South Korea has
implemented a probation system that improves criminality in accordance with volunteer
activities and attendance center orders, while living a normal life at home, school, and
the workplace, and without imprisoning teenagers who commit crimes [1]. In the case
of juvenile crimes, the premise is that these individuals are not fully developed when
compared to adults; therefore, delinquency is managed through protection and education,
rather than strong punishment [2].
Youth crime rates continue to decline due to the efforts of programs for adolescents
under probation. In 2018, the number of probationary teenagers stood at 35,626, 4.2% less
than that in the previous year. Also, the proportion of teenagers who received their first
probation in the past decade accounted for 48.3% in 2018, compared to 66.1% in 2009 [3].
However, unlike the declining trend of probationary teenagers, there remains work to be
done regarding juvenile delinquency. According to the crime white paper of the Ministry of
Justice [4], the proportion of crimes by women is increasing based on the status of probation
in 2018, and 16- to 17-year-olds account for the highest percentage of all criminal and special
law crimes. The highest numbers of charges were for theft (11,625; 34.9%) and violence
(4207; 12.6%). In particular, the biggest problem is that approximately 90% of all repeat
offences occur within a year. In 2018, Korea’s crime rate for probationary teenagers was
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105467
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
2 of 15
15.7% within one month, 24.1% within three months (one to three months), 23.4% within
six months (three to six months), and 26.4% within a year (six months to one year), with a
total crime rate of 89.6%. This shows that the target number of probationary teenagers is
much higher than that of adults. To solve these problems, an important strategy involves
improving the attendance center order programs for probationary youth.
Adolescence is the stage of life in which people experience the most risks, opportuni-
ties, frustrations, and achievements [5]. According to Ryff [6], psychological well-being is
the sum of psychological aspects constituting an individual’s quality of life. People with
a high quality of life accept themselves as they are and maintain positive interpersonal
relationships. They can control their behavior, surrounding, sense of purpose, and motiva-
tion to reveal their potential [7]. Armsden and Greenberg [8] reported adolescents with
healthy attachments to parents and peers reported higher self-esteem and life satisfaction;
occurrences of depression, anxiety, guilt, anger, alienation, and self-concept confusion were
lower. Kim et al. [9] reported that these relationships add to the experience of school life,
as good relationships are related to high satisfaction with school. Psychological well-being
in adolescence allows young people to grow and form their judgments independently.
Receiving good social support from relationships with family and peers are important
factors that affect personal development and psychological health [10–12].
However, compared to adolescents who come from stable environments, juvenile
offenders usually hail from vulnerable environments, where their psychological, familial,
peer group and social resources are insufficient for healthy growth and development. Diffi-
culties in emotional support due to specific family structures such as single parents, divorce,
or remarriage [13–15], inconsistent parenting [16,17], deviant peer on delinquency [18],
depression [19,20], low self-concept [21], impulsiveness, and aggression [22–24] are factors
that increase juvenile delinquency. It is expected that criminals in this situation experience
low levels of happiness and high levels of psychological anxiety. The stigma of being
labeled a criminal is a stressor for juvenile offenders and is related to their depression and
low self-esteem [25,26]. Low self-esteem is a powerful influencer of violent behavior [27].
According to Lim et al. [28], the negative emotional experience of juvenile offenders affects
impulsive behavior and aggression, which directly affects delinquency. If juvenile delin-
quents fail to properly deal with stress reactions such as depression, dissatisfaction, social
contraction, and aggression, they will show problems such as drinking, drug use, running
away from home, suicide, and smoking [29,30]. The continuation of this life can be said to
affect the stress control of juvenile offenders.
The influence of stress may vary depending on how stress coping resources control
stress [31]. High levels of stress coping resources in stressful situations can buffer the
negative effects of stress. However, juvenile delinquents who have lower stress response
capabilities than ordinary teenagers are bound to be poor at coping with stress, which
can negatively affect even physical reactions. Stress and physical symptoms showed a
static correlation [32,33]. Stress reactions can be identified through autonomic neuronal
activity. In situations such as negative emotions or stress imposition, sympathetic nerve
activity increases, and parasympathetic nerves are activated when positive emotions are
triggered. If a stressful situation persists, it is difficult to maintain a balanced life between
mind and body. Therefore, it is necessary to properly manage the emotional tension of
juvenile delinquents to relieve stress-induced physical tension.
However, the current attendance center orders require a professional program that
deals with emotional and physical stability as much as retraining to prevent re-offending
and help young probationers develop healthy growth in the form of group therapy such as
mental development training, human relationships, sex education, and substance abuse
education [34]. To this end, the Ministry of Justice actively links government ministries and
private resources to promote more effective delinquent behavior correction and prevention
of recidivism through experiential learning, volunteer work, cultural arts programs, etc.
Recently, a program has been developed to help the unstable situation of probationary
youth considering their characteristics [35–38]. Attempts by various programs, such as

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
3 of 15
mentoring, art therapy, and meditation, have shown effects such as stabilizing emotions,
reducing impulsiveness and aggression, and improving empathy among teenagers, and as
a result, factors affecting delinquent behavior have improved.
According to a report by Lee et al [39], subjective evaluations of probationary ado-
lescents were conducted on the attendance center orders program. As a result, leisure
culture and hobby-based activities were most helpful in reducing delinquency behavior
and stabilizing psychology and emotions. Motivation for participation was also found to
have a higher preference for dynamic activities centered on experience or play than lecture
ceremonies. Probationary teenagers are being treated in the form of internal treatment.
The need to develop various programs aimed at recovering risk factors for youth, such as
self-esteem, sociality, and mental balance, is constantly mentioned to overcome difficulties
in daily life and to return to society smoothly.
Interest in forest activity intervention is increasing day by day to help teenagers par-
ticipate in effective attendance center order programs. Forest activities are known to play
a positive role as a space for psychological and physical recovery. It has been reported
that forest activities relieve negative emotions, such as depression and anger [40–42] and
provide stress recovery [43–45]. These positive psychological effects create positive physi-
ological effects, such as parasympathetic nerve activation [42,46–49] and stress hormone
reduction [49,50]. In addition to solely experiencing the forest, research on the effectiveness
of mental and physical health promotion activities is also underway through a program
that is systematically organized using the sounds, scents, landscapes, and natural objects
of the forest. This is also applicable to forest therapy programs for teenagers.
Forest therapy programs use physical activities and psychotherapy to help improve
the health of adolescents. Forest activities can give physical energy to teenagers. Through
various activities using natural objects, teenagers experience a sense of achievement, fun,
and immersion, and improve their concentration. Through this, teenagers’ confidence and
personal capabilities can be increased, and their interpersonal capabilities can be enhanced
through cooperation and intimacy with the members who worked together [51]. According
to Chang et al. [52], forest experience programs have been shown to help adolescents
adapt and cope by reducing depression and anxiety and positively impacting their self-
concept. Cho et al. [53] conducted forest education programs in spring, summer, and
autumn and showed improvements in adolescents’ psychological well-being and reduction
of stress levels, regardless of the season. Forest education programs also appear to effect
physiological changes. Lee [54] studied the impact of Natural Park experiences on heart
rate variability (HRV) and found that parasympathetic nerve activity was activated and
sympathetic nerve activity, which is activated under stress, was inhibited. Furthermore,
Chung et al. [55] studied a three-night and four-day forest therapy camp, considered to
be a special group, and found changes in resilience, interpersonal relationships, and heart
rate intervals. It was revealed that the forest experience not only had a positive impact
on adolescents’ development of social sentiments, such as emotional acceptability and
improved emotional control, but also provided physiological stability.
Studies of juvenile offenders with forest experience also showed potential psychologi-
cal healing [56–60]. A study by Eom et al. [56] reported that a two-day forest education
program had a positive effect on the mood, self-esteem, and self-control of probationary
youth. Jang et al. [57] reported that forest education programs showed positive changes
in self-esteem and resilience. Walsh [58] reported that program activities in nature have
shown great changes in young offenders’ hopes, resilience, and self-efficacy.
These previous studies show that forest therapy helps develop prosocial connections
and bonds and introduces positive psychological and physiological stimuli for juvenile
offenders. However, there is still a lack of underlying research to help young people with
psychological and physical stability through forest therapy programs, and more evidence
on health benefits is needed. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate whether forest
therapy developed by referring to the characteristics of probationary adolescents affected
their psychological and physical conditions.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
4 of 15
Hypothesis 1. Adolescents under probation who have experienced forest therapy programs will
see a greater positive change in their psychological well-being in comparison to those who have
attendance center orders.
Hypothesis 2. Adolescents under probation who have experienced forest therapy programs will
show a greater positive change in HRV than those who have attendance center orders.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
The program was conducted with 50 juvenile probationers from the Gyeonggi Justice
Compliance Support Center. This study was conducted with the approval of the IRB
(CBNU-201809-SB-711-01) of Chungbuk National University Industry–Academic Coopera-
tion Foundation. The researcher made a recruitment announcement to a Justice Compliance
Support Center in Korea to conduct a forest therapy program for probationary youth. After
a meeting with a Justice Compliance Support Center that expressed its willingness to
participate in the program and the overall progress of the program, the probationary youth
were notified of the recruitment. Participants were selected from those who completed a
voluntary participation agreement after explaining the purpose and content of the study.
The forest therapy program was conducted in different groups of participants, and in the
case of the experimental group, the two-day, one-night program was divided into 8 people
in the first, 9 people in the second, and 13 people in the third. The control group had
17 participants in two days.
Most of the juvenile probationers who participated in the study identified as “male”
(92.5%). The age range was 15 to 20 years old. The average age of the experimental
group was 16.4 years, and of the control group was 15.8 years. Participants included
14 middle school students (experimental group N = 8, control group N = 6) and 36 high
school students (experimental group N = 25, control group N = 11). An overview of the
demographic data is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of experimental and control groups.
Classification
Sex
Age average
Academic
Background
Male
Female
1999–2003
Middle school
enrolled
High school
enrolled
Experiment Group (N = 33)
N (%)
32 (68.1%)
1 (33.3%)
16.4
8 (55.0%)
25 (71.5%)
Control Group (N = 17)
N (%)
15 (31.9%)
2 (66.7%)
15.8
6 (45.0%)
11 (28.5%)
Total
N (%)
47 (100.0%)
3 (100.0%)
16.1
14 (100.0%)
36 (100.0%)
2.2. Experimental Sites
The Saneum Healing Forest is the first healing forest in Korea. It is composed of
various tree species, such as pine (Pinus Densiflora Siebold & Zucc), larch (larix kaempferi
(Lamb.) Carrière), and ash (fraxinus rhynchophylla), among others. The natural environment is
excellent. The altitude of Saneum Healing Forest varies from about 200 to 1000 m, making
it suitable for forest therapy programs using climate and exercise therapy. The valley,
which has abundant water resources, is located around the Health Promotion Center. By
generating anions, Healing Forest Road is known to make people feel increased immune
health, mental stability, and freshness. The Saneum Healing Forest is a suitable destination
for forest therapy based in sensory programs (see Figure 1).

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
5 of 15
Figure 1. The Saneum Healing Forest.
2.3. Procedure
The forest therapy program ran from August to September 2018. The study explored
the effectiveness of a non-randomized control group pretest–post-test design forest therapy
program. The forest therapy program was conducted for two days and one night for the
experimental groups (N = 33), who participated in the forest therapy program, and the
control group (N = 17), who received two days of an attendance center orders program. A
pretest measurement was conducted before the forest therapy program began. On the first
day, participants arrived at the Healing Forest Center to understand the questionnaire, fill
out the psychological well-being questionnaire, and measure their HRV. After the pretest,
the schedule for the next two days and one night was introduced, with precautions for
safety. Participants placed their luggage in their accommodations, finished their lunches,
took a break, and began the forest therapy program. After the first day of the program, they
stayed overnight at the Saneum Recreation Forest and proceeded with the program the next
morning. After sharing their impressions, the program ended. The questionnaires were
filled in and HRV was measured. After these were completed, the participants returned
home with a probation officer.
The program consisted of three themes, and its purpose was to observe positive
psychological and physical changes through activities in the forest. The first theme, “Go
to the Forest” (“body, hello!”, “introduce myself using natural objects”), was designed to
raise interest in forests, form intimacy between participants, and prepare participants to
adapt to the new environment. The second theme, “Do in the Forest” (“sense awakening
walk”, “dream of trees”, “my dream”, “meditation with walking in forest: slow pace”,
“looking at the sky”, and “night walk in the forest”) aimed at relaxing the mind and body
through walking in the forest and meditating in the forest environment through five senses.
Moreover, they were encouraged to reflect on the past and think about the future. The
final theme, “With the Forest and Well” (“storytelling: my dream”, “phytoncide breathing
meditation”, “hammock healing”, “scent of forest therapy), was designed to provide an
opportunity to define dreams and visions for the future (see Figure 2).

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
6 of 15
Figure 2. Major progress of forest therapy program.
The forest therapy program was conducted by two forest therapy instructors. Two
probation officers participated in the program to encourage lagging participants. They
participated in the play to increase the participants’ immersion and to safeguard the
participants. Each program’s progress time and unit program were adjusted according
to the participant’s immersion or condition. Detailed forest therapy program activities
were scheduled as shown in Table 2. Participants in the control group visited the Ministry
of Justice Compliance support center for two days and were required to carry out the
attendance center orders program. Pre- and post-measurements were performed in the
same way as the experimental group. The control group was instructed to continue general
life routines, except for visiting the natural environment.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
7 of 15
Table 2. Forest therapy program.
Time
07:00-
08:00–09:00
Day 1
09:00–11:00
11:00–12:30
12:30–13:30
13:30–14:00
14:00–15:00
15:00–15:40
15:40–16:20
16:20–17:00
17:00–18:00
18:00–19:30
19:30–20:50
20:30-
-Orientation and fill in the consent form
-Physiological and psychological pretest
Lunch
Check in
-Body, hello! (Forest gym exercise)
-Introduce myself using natural objects
Sense awakening walk
-Dream of trees (investigating organic and
dynamic ecological links of forest)
-My dream (cutting logs and watching their
growth rings)
Meditation with walking in forest: slow pace
Looking at the sky
Dinner
Night walk in the forest
Free time and off to dream land
Day 2
-Get up
-Morning walk
Breakfast
-Storytelling: my dream
-Hammock healing
-Scent of forest therapy
-Physiological and
psychological posttest
Lunch
2.4. Measurement
2.4.1. Psychological Well-Being (Well-Being Manifestation Measure Scale)
To measure the psychological well-being of adolescents, Park and Choi [61] translated
and calibrated into Korean the Well-Being Manifestation Measure Scale developed by
Masse et al. [62]. The subfactor of this scale is the five-point Likert scale (1 = strongly
disagree; 5 = strongly agree), consisting of a total of six subfactors and 25 questions
measuring self-esteem, mental balance, sociability, social involvement, control of self and
events, and happiness. The higher the score of each question, the higher the level of
psychological well-being of adolescents. The Cronbach’s α of the original measurement
was 0.92.
2.4.2. HRV
The HRV test is a method of measuring the reaction of the autonomic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is activated during experiences of tension and stress,
and the parasympathetic nervous system activates during relaxation. The activities of
the autonomic nervous system and the sympathetic nervous system are measured by
analyzing the power spectrum for the change in the interval. HF (high frequency) indicates
the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, and LF/HF (a ratio of Low Frequency
to High Frequency) indicates the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic
nervous systems. In this study, participants were measured in comfortable sitting positions
for three minutes using uBioMacpa(Biosense creative, Seoul, Korea) instruments.
2.5. Data Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 21.00 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). A
response paired sample t-test was performed to identify changes in psychological well-
being and HRV between the pre- and post-test. ANCOVA was conducted to compare
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
8 of 15
differences between groups (experimental and control). The pretest results were used as
covariates (baseline data) to eliminate the effects of different levels of individual psycho-
logical well-being and HRV. All statistical tests were performed at a significance level of
p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Psychological Well-Being (Well-Being Manifestation Measure Scale)
3.1.1. Results of Measurement for Pre- and Post-Test Psychological Well-Being
The results of paired t-tests between pre- and post-tests, which verified how affected
the psychological well-being for each group presented in Table 3. The results showed
that forest therapy programs had a positive effect on the psychological well-being of
juvenile probationers. The psychological well-being score of the probationary youth who
participated in the forest therapy program increased significantly (t = −5.64, p = 0.000).
Among the subfactors of psychological well-being, self-esteem (t = −4.66, p = 0.000),
mental balance (t = −4.37, p = 0.000), social involvement (t = −4.31, p = 0.000), sociability
(t = −3.13, p = 0.004), control of self and events (t = −5.73, p = 0.000), and happiness
(t = −5.53, p = 0.000) showed improvement in the mean value improved and showed
significant results. Conversely, the control group did not show effects on the psychological
well-being of juvenile probationers. Control group did not change significantly, not only in
psychological well-being, but also in subfactors such as self-esteem, mental balance, social
involvement, sociability, control of self and events, and happiness.
Table 3. Comparison of pre- and post-tests for psychological well-being between the experimental and control groups.
Variable
Psychological
well-being
Subfactor
Experiment Group (N = 33)
Pretest
M ± SD
Post-Test
M ± SD
t
Control Group (N = 17)
Pretest
M ± SD
Post-Test
M ± SD
t
Self-esteem
3.30 ± 0.86 4.01 ± 0.71 −4.66 *** 3.40 ± 0.77 3.26 ± 0.73 2.08
Mental balance
3.18 ± 0.83 3.85 ± 0.70 −4.37 *** 3.33 ± 0.73 3.22 ± 0.61 1.13
Sociability
3.13 ± 0.80 3.77 ± 0.65 −4.31 ** 3.34 ± 0.51 3.21 ± 0.75 1.09
Social involvement
3.48 ± 0.89 3.96 ± 0.70 −3.13 *** 3.41 ± 0.59 3.18 ± 0.54 0.75
Control of self and events 2.97 ± 0.88 3.83 ± 0.69 −5.73 *** 3.25 ± 0.54 3.22 ± 0.50 1.59
Happiness
3.12 ± 1.01 3.90 ± 0.61 −5.53 *** 3.47 ± 0.58 3.24 ± 0.46 0.27
Total
3.19 ± 0.78 3.90 ± 0.61 −5.64 *** 3.37 ± 0.46 3.22 ± 0.46 2.12
M = mean; SD = standard deviation ** p < 0.01 *** p < 0.001 by paired t-test.
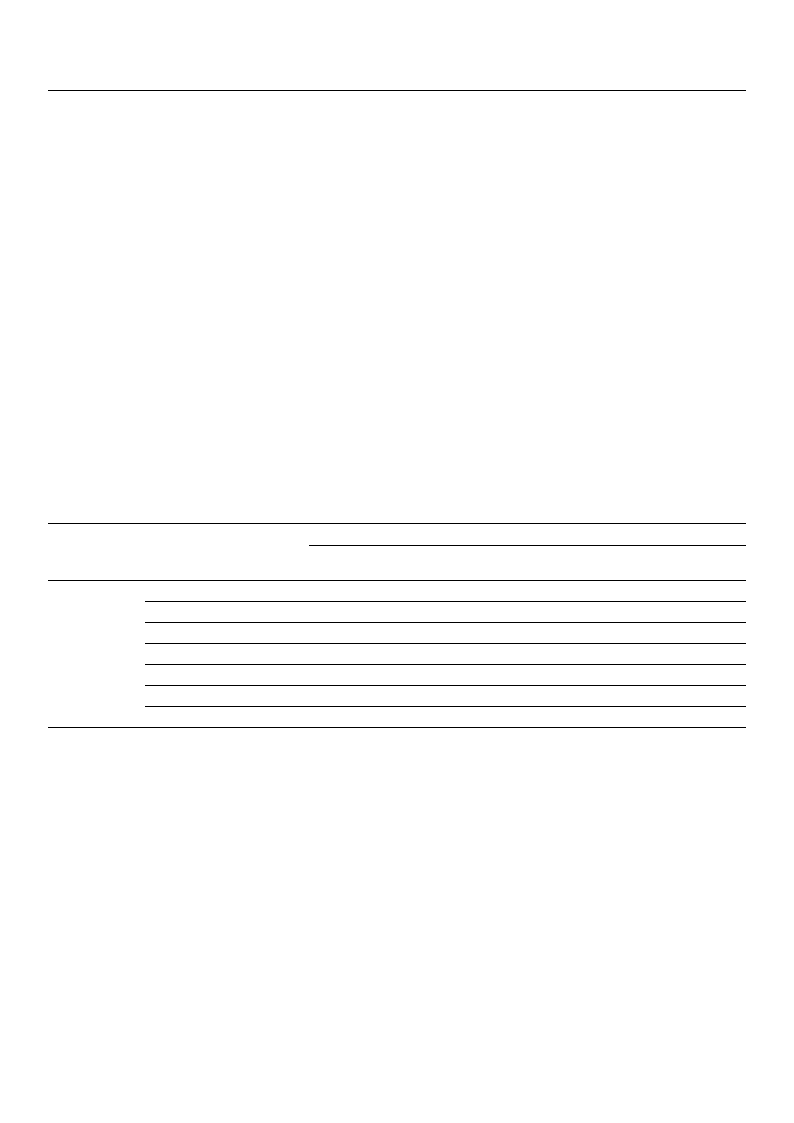
3.1.2. Results of Psychological Well-Being Measurement in Each Group
To examine the effects on juvenile probationers’ psychological well-being, a covariance
analysis (ANCOVA) was conducted to compare the different values before and after the
program experience for each group (see Figure 3). It was confirmed that the forest therapy
program resulted in positive changes in psychological well-being (F = 27.348, p = 0.000).
In the verification of the subfactors of psychological well-being, the experimental group
that attended the two-day/one-night forest therapy program showed a positive change in
self-esteem (F = 18.018, p = 0.000), mental balance (F = 14.929, p = 0.000), social involvement
(F = 10.163, p = 0.003), sociality (F = 18.019, p = 0.000), control of self and events (F = 17.047,
p = 0.000), and happiness (F = 25.787, p = 0.000).
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
9 of 15
Figure 3. The effect of forest therapy on psychological well-being, comparing experimental and
control groups, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.2. HRV
3.2.1. Measurement Results for Pre- and Post-Test HRV
The results of paired t-tests between pre- and posttests, which verified how affected
the HRV for each group presented in Table 4. HF and LF/HF show the activity of parasym-
pathetic nerves, which is an indicator of HRV. The forest therapy program participation
group showed positive changes in HF (t = −3.77, p = 0.001) and LF/HF (t = 4.38, p = 0.000).
The juvenile probationers’ activity in the forest was physiologically stable and positively
affected. Conversely, the control group did not show effects on the HF or LF/HF of
juvenile probationers.
Table 4. Comparison of HRV pre- and posttests between the experimental and control group.
Variable
Experiment Group (N = 33)
Pretest
M ± SD
Post-Test
M ± SD
t
Control Group (N = 17)
Pretest
M ± SD
Post-Test
M ± SD
HRV
HF 6.98 ± 0.64 7.32 ± 0.54
LF/HF 1.18 ± 0.11 1.09 ± 0.09
−3.77 **
4.38 ***
6.91 ± 0.66
1.20 ± 0.13
M = mean; SD = standard deviation ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by paired t-test.
7.03 ± 0.31
1.15 ± 0.08
t
−1.15
1.37
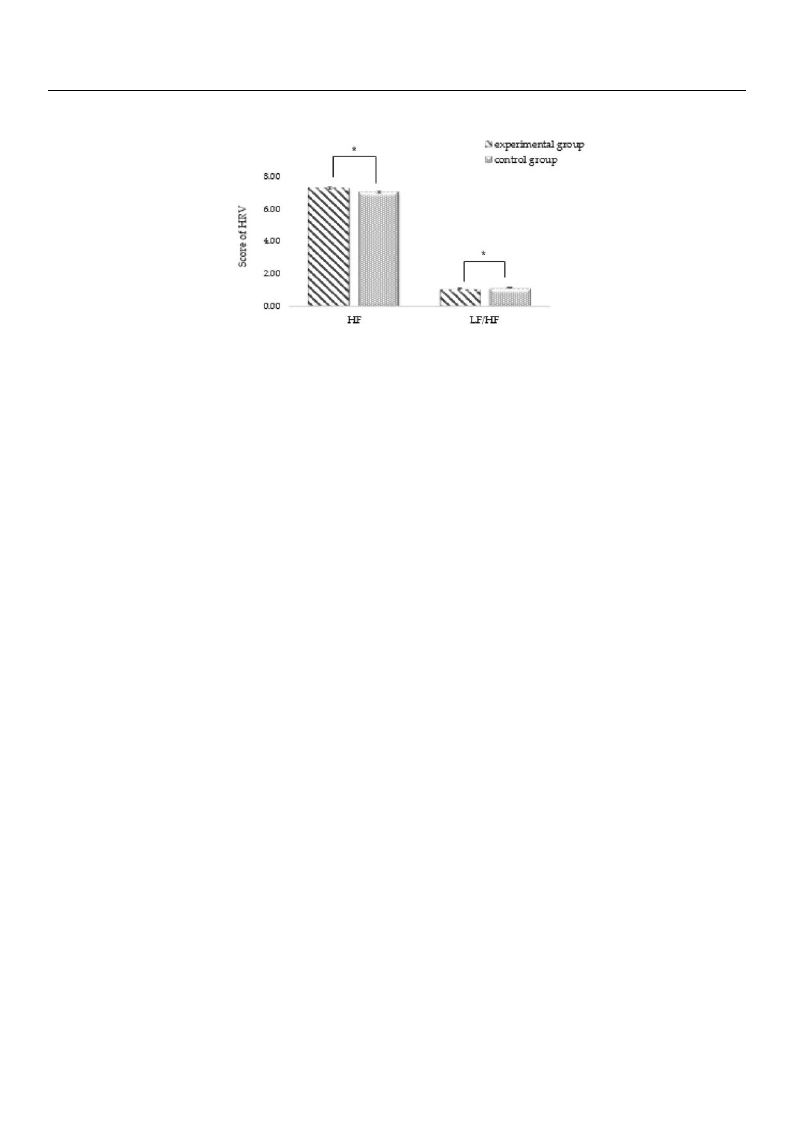
3.2.2. Results of HRV Measurement in Each Group
ANCOVA was conducted to compare the value differences between pre- and post-
HRVs and identify physiological changes between the different program groups. As a
result of HF, a positive change (F = 5.280, p = 0.026) was observed in adolescents who
received forest therapy. In the experimental group, LF/HF also showed a positive effect
(F = 4.848, p = 0.033) (see Figure 4). The forest environment creates comfort for the human
body, and this positively affects physiological changes. It has been shown that forest
therapy participants can achieve emotional stability through autonomic nervous system
balance and parasympathetic nerve activation.
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
10 of 15
Figure 4. The effect of forest therapy on HRV by comparing experimental and control groups,
* p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
This study was conducted to promote the psychological and physical stability of
probationary youth by participating in a camp-type forest therapy program, which was
organized to reflect their characteristics, for two days and one night. The results of this
study showed that the forest therapy program influenced the psychological well-being and
physical health of probationary adolescents. Empirical studies show that forest therapy
programs, as well as simple activities in the forest, affect the health of participants. However,
few studies have reported the psychological and physical effects of forest therapy programs
for adolescents under probation. Therefore, this study suggests that these programs can
help improve the psychological and physical health of probationary adolescents.
The results of the effectiveness of forest therapy programs for adolescents under
probation are as follows: First, the experimental group that received the forest therapy
program experienced a significant improvement in psychological well-being after the
program. Self-esteem, mental balance, social involvement, sociability, control of self and
events, and happiness, which are components of psychological well-being and have greatly
improved. However, there were no significant changes in the control group. These results
are consistent with prior studies that show that activities in forests have a positive effect on
the psychological well-being [63–65]. Kim et al. [63] showed a change in the psychological
well-being of high school students who received forest therapy programs using school
forests and the attitude toward forests. You et al. [64] reported that a forest therapy program
helped relieve psychological well-being, depression, and stress. Lee et al. [65] reported
that forest healing programs improved participants’ psychological well-being, optimistic
personal relationships, autonomy, and purpose of life. Juvenile delinquents experience
more negative than positive emotions. According to a study by Shin et al. [66], the forest is
a place where one can experience pleasure and self-realization by performing activities that
create a sense of accomplishment, exploration, and adventure (in line with the pleasure of
flow). This suggests that forests produce a restoration effect, reducing negative emotions
and shifting emotional states [40–42]. Furthermore, active forest intervention may have a
positive effect on the psychological well-being of probationary adolescents.
Second, the experimental group that received the forest therapy program experienced
significant improvement in HRV’s HF and LF/HF physiological stability after the forest
therapy program. However, there was no significant change in the control group. This
was consistent with the findings of prior studies that forest activities provide physiological
stability through the activation of parasympathetic nerves [42,46–49,67,68]. A stress is a
process by which a person responds with specific physiological responses and actions to
situations that threaten their well-being and health [69]. In situations of excitement and
stress, sympathetic nerves are activated, increasing heart rate, and maintaining tension;
it is, therefore, important to activate the parasympathetic nerves so that the body can
stabilize. Woo et al. [67] reported a significant increase in parasympathetic nerves (HF)

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
11 of 15
after conducting a forest therapy program for patients with depression. According to
Li et al. [68], autonomic neuronal balance (LF/HF) and stress index significantly decreased
after experiencing a long-term forest therapy program (six nights and seven days). Activi-
ties in the forest help stabilize the body and mind. Quintana et al. [70] reported that the
social and cognitive ability to understand other people’s feelings, thoughts, etc. was report-
edly superior to that of other students when the parasympathetic nerves were activated.
Sensitive and nervous adolescents’ emotions can negatively affect their physical responses
and are thought to have a positive effect on the physiological stability of probationary
adolescents with aggressive and spontaneous characteristics.
Third, there was a clear difference between the forest therapy group and the control
group. The forest experience not only positively affected the development of social emo-
tions, such as emotional acceptance and improved emotional control of teenagers, but
also provided physiological stability. Forest therapy played a role in reducing stress from
everyday life. The program intervention, which combines the healing elements of nature
to help subjects improve their activities in the forest, is likely to have promoted physical
stability changes, increasing their resilience in the natural environment.
The forest therapy experience for probationary youth affected not only their emotional
stability, but also their mental and physical resilience. Forest therapy played a role in
reducing stress from everyday life. These programs may improve adolescents’ positive
thinking toward the future along with an increased sensitivity or sense of cooperation with
others. All these factors contribute to character development and personal growth. Such
programs can play an active role in improving mental health and for reaching target goals
for probationary youth. Forest therapy programs are not passive activities. Instead, par-
ticipants experience the forest through meditation, physical activity, mental and physical
relaxation, and ecological education. This mental health service provided to adolescents
has a significant impact on delinquency behaviors and reducing recidivism [71,72]. Thus,
adolescents with weak social ties and low empathy can experience changes as these pro-
grams reduce aggression and encourage group cooperation. Participation in the camp-like
forest therapy program may ultimately help with social participation, social improvement,
and relationships with others. Adolescence is a time when emotional instability, extreme
emotions, and emotional intensity are at their highest point [73]. Considering that this is
the time when emotional and physiological health is responsive to psychological stability,
the forest therapy program can provide a sense of psychological relaxation. Further imple-
mentation as an attendance center orders program will ultimately have a positive effect on
crime prevention and juvenile guidance.
Several limitations exist in this study. First, it is difficult to identify and present a
suitable period for the effectiveness of participants in the detailed program with a program
that lasted for one night and two days. Further research is needed to clarify the effects of
the participation period and the continued effectiveness of the program after returning
to daily life. Second, the sample size was small, and there are limitations to generalizing
the results. Therefore, further research is needed for a variety of participants, depending
on the type and motivation, characteristics of the individual offenses. In the case of
juvenile delinquents, there are various factors that affect crime. Therefore, different types
of interventions are needed. Third, participants’ experience, satisfaction, and preferences
in the forest can affect the results. Due to the participants’ satisfaction with the forest, it
can be difficult to see it as an effect of the forest therapy program alone. Fourth, there was
minimal control over the daily activities of the control group. The types of activities other
than program activity hours in the control group (i.e., academic, family, peer relations,
etc.) may have varied, which may have affected the outcome comparison. Fifth, a deeper
approach is needed to discuss new possibilities for the psychological and physical well-
being of probationary adolescents. Additional research using qualitative analysis is needed
to understand the process of changes in an individual’s emotions and cognition through
forest therapy programs. In addition, longitudinal studies on the changes in participants
will also be needed. These limitations should be considered for future research.

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
12 of 15
Nevertheless, this study is significant in that it verified the applicability and effective-
ness of forest therapy programs with special groups of youth guardians. Future studies
should organize various forms of forest therapy programs tailored to the individual needs
and goals of probationary youth. It is reported that the forest therapy program will
contribute to the social and emotional development of probationary youth, which is the
purpose of the probation system.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study show that forest therapy can help improve the psychologi-
cal and physiological symptoms of emotionally unstable juvenile probationers, who are
establishing themselves in various experiences at this stage of life. Therefore, forest ther-
apy can contribute to emotional stability and health promotion if it is used to manage
psychological stability.
Author Contributions: J.Y.J. performed data acquisition, statistical analysis, interpretation of the
results, and manuscript preparation. I.O.K. was involved with data acquisition and performed a forest
therapy program. P.-s.Y. contributed to statistical data analysis and interpreted the results. W.S.S. led
the research process, experimental design, interpretation of results, and manuscript preparation and
editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding: This research received the support of “juveniles on probation forest education consignment
business” provided by the Korea Forest Service.
Institutional Review Board Statement: This study was conducted with the approval of the IRB
(CBNU-201809-SB-711-01) of Chungbuk National University Industry–Academic Cooperation Foun-
dation.
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement: The data presented in this study are available on request from the
corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments: We offer profound thanks to the forest therapy instructors for their valuable guid-
ance.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
1. Lee, I.G. On the Measures to Ensure the Effectiveness of the Korean Boys’ Probation System-Focusing on the Need for Legal
Education. Law Rev. 2020, 20, 313–341.
2. Park, H.H.; Kim, J.H. A Study on the Discussion of the Amendment of the Juvenile Act—Focussing on the Reinforcement of
Juvenile Protection Ideology. Dong A Law Rev. 2018, 78, 1–26. [CrossRef]
3. Korean National Police Agency. Crime Phenomenon and Criminal Policy in Korea (2019); Korean National Police Agency: Seoul,
Korea, 2020.
4. Institute of Justice. The White Paper on Crime 2019; Institute of Justice: Jincheon, Korea, 2020.
5. Erikson, E.H. Identity Youth and Crisis; WW Norton: New York, NY, USA, 1968.
6. Ryff, C.D. Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol.
1989, 57, 1069–1081. [CrossRef]
7. Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.W.; Cha, K.H. Analyses on the Construct of Psychological Well—Being (PWB) of Korean Male and Female
Adults. Korean J. Soc. Personal. Psychol. 2001, 13, 19–39.
8. Armsden, G.C.; Greenberg, M.T. The Inventory of Parent and Peer Attachment: Individual Difference and Their Relationship to
Psychological Well-Being in Adolescence. J. Youth Adolesc. 1987, 15, 227–254. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
9. Kim, A.K.; Kim, S.B. Effects of Parent Attachment, Peer Attachment, Teacher Attachment, and Ego Resilience on Adolescents’
School Life Adjustment. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2018, 25, 273–297. [CrossRef]
10. Laird, R.D.; Criss, M.M.; Pettit, G.S.; Dodge, K.A.; Bates, J.E. Parents’ monitoring knowledge attenuates the link between antisocial
friends and adolescent delinquent behavior. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2008, 36, 299–310. [CrossRef]
11. Ingram, J.R.; Patchin, J.W.; Huebner, B.M.; McCluskey, J.D.; Bynum, T.S. Parents, friends, and serious delinquency: An examination
of direct and indirect effects among at-risk early adolescents. Crim. Justice Rev. 2007, 32, 380–400. [CrossRef]
12. Ciarrochi, J.; Morin, A.J.; Sahdra, B.K.; Litalien, D.; Paker, P.D. A longitudinal person-centered perspective on youth social
support: Relations with psychological wellbeing. Dev. Psychol. 2017, 53, 1154–1169. [CrossRef]

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
13 of 15
13. Shader, M. Risk Factors for Delinquency: An Overview; Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Office of Juvenile Justice
and Delinquency Prevention: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
14. McCord, J.; Widom, C.S.; Crowell, N.A. Juvenile Crime, Juvenile Justice. Panel on Juvenile Crime: Prevention, Treatment, and Control;
National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
15. Chin, T.W.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.P.; Cho, S.C. The influence of family environment and moral development to conduct disorder in
adolescents. J. Korean Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1997, 8, 163–174.
16. McPhail, L.M. Early Intervention for Stealing: Interrupting the Antisocial Trajectory. Master’s Thesis, University of Canterbury,
Christchurch, New Zealand, 2008.
17. Lee, E.G.; Han, S.Y. Effects of Affection, Monitoring and Inconsistent Parenting on the Emotional Problems of Children and
Adolescents. Korean J. Hum. Dev. 2016, 23, 153–172.
18. Lee, S.M. The Effects of Deviant Peer on Delinquency: The Difference of Gender and an Opposite Sex Peer. J. Korean C. Assoc.
2018, 12, 47–71.
19. Son, S.O.; Lee, B.J. A Study of Influencing Factors of adolescent social relations: Examining the Mediating Effects of Aggression
and Depression, and gender differences. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2015, 22, 1–26.
20. Cheng, H.; Furnham, A. Personality, self-esteem, and demographic predictions of happiness and depression. Personal. Individ.
Differ. 2003, 34, 921–942. [CrossRef]
21. Levy, K. The relationship between adolescent attitudes towards authority, self-concept, and delinquency. Adolescence 2001, 36,
333–346.
22. Farrington, D.P.; Biron, L.; LeBlane, M. Personality and delinquency in London and Montreal. In Abnormal Offenders, Delinquency,
and the Criminal Justice System; Gunn, J.C., Farrington, D.P., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982.
23. Achenbach, T.M. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4–18 and 1991 Profile; University of Vermont: Burlington, VT, USA, 1991.
24. Tremblay, R.E.; Nagin, D.S.; Séguin, J.R.; Zoccolillo, M.; Zelazo, P.D.; Boivin, M.; Pérusse, D.; Japel, C. Physical aggression during
early childhood: Trajectories and predictors. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e43–e50. [CrossRef]
25. Park, B.S.; Bae, S.W.; Jin, H.M. The impact of informal Labeling, self-esteem, depression, and aggression on juvenile delinquency-
Focusing on path analysis. J. Adolesc. Welf. 2011, 13, 121–148.
26. Park, D.J.; Kim, N.Y. Mediating Effects of Self-Esteem on the Effects of Social Stigma on Depression of Out-of-School Adolescents.
J. Youth Act. 2019, 5, 71–87.
27. Anderson, E. The code of the streets. Atl. Mon. 1994, 273, 81–94.
28. Lim, J.S.; Han, M.I.; Han, E.Y. Factors Influencing the Aggression Levels of Juvenile Offenders Using the Heckman Selection
Model. Stud. Korean Youth 2009, 20, 29–69.
29. De Wilde, E.J.; Kienhorst, C.W.; Diekstra, R.F.W.; Wolters, W.H.G. The relationship between adolescent suicidal behavior and life
event in childhood and adolescence. Am. J. Psychiatry 1992, 149, 45–51. [PubMed]
30. Nam, J.S. The Relationship between Participation in Leisure Sports Activities of middle and high School Students and Pro-Social
Behavior. Master’s Thesis, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea, 2004.
31. Wheaton, B. Models for the stress-buffering functions of coping resources. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1985, 26, 352–364. [CrossRef]
32. Seo, J.Y.; Kim, M.Y. Stress, physical symptoms, and coping styles of high school students. Child Health Nurs. Res. 2006, 12, 470–477.
33. Bang, K.S.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J. A Comparison of Mental Health of School Age Children between Urban and
Rural Area and a Correlation Analysis of Subjective Mental Health Indicators and Heart Rate Variability. J. Korean Soc. Sch. Health
2017, 30, 266–273.
34. Lee, M.S. Current Status and Vitalization Plan of Juvenile Probation. Korean Juv. Prot. Rev. 2020, 33, 159–185.
35. Lee, G.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Song, J.Y.; Jeon, J.H. The effectiveness of prevention program of recidivism for school violence on juvenile
probation focusing on the empathy development training program. Korean J. Probat. 2013, 13, 249–274.
36. Kweon, H.S. The effect of a mentoring program on fostering positive development capabilities in juveniles under probation. J.
Korea Inst. Youth Facil. Environ. 2014, 12, 81–92.
37. Lee, J.H.; Ryu, J.M. The effect of group art therapy using mandala for emotional stabilization and attentiveness of juvenile
delinquents. Korean J. Arts Ther. 2014, 14, 41–66.
38. Kim, I.S. Tea-culture therapy program development to alleviate the aggressiveness of the juvenile probationers. Korean J. Probat.
2017, 1, 123–151.
39. Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, S.J. Study on the Status of Educational Guidance of At-Risk Youths and Measures Enhance its
Efficacy; National Youth Policy Institute: Sejong, Korea, 2018.
40. Park, B.J.; Furuya, K.; Kasetani, T.; Takayama, N.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Relationship between psychological responses and
physical environment in forest settings. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 102, 24–32. [CrossRef]
41. Takayama, N.; Korpela, K.; Lee, J.; Morikawa, T.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.-J.; Li, Q.; Tyrväinen, L.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kagawa, T.
Emotional, restorative and vitalizing effects of forest and urban environments at four sites in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public
Health 2014, 11, 7207–7230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
42. Lee, J.; Park, B.J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Ohira, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Effect of forest bathing on physiological and psychological
responses in young Japanese male subjects. Public Health 2011, 125, 93–100. [CrossRef]
43. Jung, W.H.; Woo, J.M.; Rye, J.S. Effect of a forest therapy program and the forest environment on female workers’ stress. Urban
For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 274–281. [CrossRef]

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
14 of 15
44. Lee, J.W.; Yeon, P.S.; Park, S.H.; Kang, J.W. Effects of a forest therapy program on the stress and emotional change of emotional
labor workers. J. Korean Inst. For. Recreat. 2018, 22, 13–22.
45. Hong, J.; Park, S.; Lee, J. Changes in depression and stress of the middle-aged and elderly through participation in a forest
therapy program for dementia prevention. J. People Plants Environ. 2019, 22, 699–709. [CrossRef]
46. Park, B.J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Kasetani, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. The physiological effects of Shinrin-yoku (taking in the forest
atmosphere or forest bathing): Evidence from field experiments in 24 forests across Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15,
18–26. [CrossRef]
47. Park, B.J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Ishii, H.; Furuhashi, S.; Hirano, H.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of Shinrin-yoku
(taking in the atmosphere of the forest) in a mixed forest in Shinano Town, Japan. Scand. J. For. Res. 2008, 23, 278–283. [CrossRef]
48. Park, B.J.; Kasetani, T.; Morikawa, T.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of forest recreation in a young
conifer forest in Hinokage Town, Japan. Silva Fenn. 2009, 43, 291–301. [CrossRef]
49. Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.J.; Ishii, H.; Hirano, H.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of “Shinrin-yoku” (taking in the
atmosphere of the forest) in an old-growth broadleaf forest in Yamagata prefecture, Japan. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2007, 26, 135–142.
[CrossRef]
50. Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.J.; Miyazaki, Y. Trends in research related to “Shinrin-yoku” (taking in the forest atmosphere or forest
bathing) in Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15, 27–37. [CrossRef]
51. Oh, K.H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, Y.S. The effects of forest-healing program on developing Youth activity competence. Korean J.
Youth Stud. 2016, 23, 1–24. [CrossRef]
52. Chang, J.S.; Kim, N.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, B.S. The Forest Experience Program and Improvement of Depression, Anxiety, and
Self-concept in Adolescents. J. Korean For. Soc. 2015. 104, 127–132. [CrossRef]
53. Cho, Y.M.; Kim, D.J.; Yeon, P.S.; Kwon, H.K.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, J.M. The influence of a seasonal forest education program on
psychological well-being and stress of adolescents. J. Korean Inst. For. Recreat. 2014, 182, 59–69.
54. Lee, J.A. Study on the Stress Relief Effects of Adolescent Physical Activity in City Parks. Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University,
Seoul, Korea, 2017.
55. Chung, A.S.; Choi, S.W.; Woo, J.M.; Mok, J.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Park, B.J. The Effect of Short-term Forest Therapy Camp on Youths with
Internet Addiction Risk Group: Focused on the Biological, Neurocognitive and Psychosocial Aspects. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2015,
104, 657–667. [CrossRef]
56. Eom, M.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ha, S.Y. Effect of Forest Education Program on Juvenile Probationers’ Mood States, Self-esteem, and Self
Control. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2016, 105, 253–260.
57. Jang, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Ha, S.Y. A Study on Effect of Forest Education Program for Juvenile Probationers. J. People Plants Environ. 2017,
20, 271–282. [CrossRef]
58. Walsh, M.A. Wilderness Adventure Programming as an Intervention for Youthful Offenders: Self-Efficacy, Resilience, and Hope
for the Future. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota Digital Conservancy, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2009.
59. Ha, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Eom, M.S. Forest Education for Juvenile Probationers, KFRI Forest Policy Issues; Bulletin 50; National Institute of
Forest Science: Seoul, Korea, 2015.
60. Yoon, C.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.K.; Jeong, D.J.; Ha, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Choi, I.S.; Son, J.W. Study on the Development and Management of a
Forest Experience Program to Support the Growth of the Youth at Risk; National Research Council for Economics, Humanities and
Social Sciences: Sejong, Korea, 2014.
61. Park, E.J.; Choi, S.M. The study on a validation of well-being manifestation measure scale in Korea. Korea Youth Res. Assoc. 2014,
21, 495–511.
62. Masse, R.; Poulin, C.; Dassa, C.; Lambert, J.; Belair, S.; Battaglini, M.A. Elaboration and validation of a tool to measure
psychological well-being: WBMMS. Can. J. Public Health Revue Can. Sante Publique 1997, 89, 352–357.
63. Kim, H.R.; Koo, C.D. The Influence of Urban Forest and School Forest Experience Activities on Attitude Toward Forest,
Psychological Well-being and Stress of High School Student. Korean J. Environ. Ecol. 2019, 33, 341–353. [CrossRef]
64. You, Y.S.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, C.J.; Jang, N.C.; Son, B.K. A Study of Effects of Sallimyok (Forest Therapy)-based Mental Health
Program on the Depression the Psychological Stability. J. Korean Soc. Sch. Community Health Educ. 2014, 15, 55–65.
65. Lee, M.N.; Song, J.S. The Effects of Prenatal Education in Forest on the Mindfulness and Psychological Well-Being of Pregnant
Woman. J. Korean Inst. For. Recreat. 2015, 19, 25–34.
66. Shin, W.S. Socialization of Forests; Ddanim: Seoul, Korea, 2003.
67. Woo, J.M.; Kim, W.; Park, S.M.; Lim, S.K. Synergistic Effect of Forest Environment and Therapeutic Program for the Treatment of
Depression. J. Korean For. Soc. 2012, 101, 677–685.
68. Lee, B.; Park, C.H.; Park, S.J. Effect of Long-Term Stay Forest Therapy Program on User’s Positive and Negative Emotions and
Physical Changes. J. Korean For. Soc. 2020, 109, 544–552.
69. Ulrich, R.S.; Simons, R.F.; Losito, B.D.; Fiorito, E.; Miles, M.A.; Zelson, M. Stress recovery during exposure to natural and urban
environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 1991, 11, 201–230. [CrossRef]
70. Quintana, D.S.; Guastella, A.J.; Outhred, T.; Hickie, I.B.; Kemp, A.H. Heart rate variability is associated with emotion recognition:
Direct evidence for a relationship between the autonomic nervous system and social cognition. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 86,
168–172. [CrossRef]

Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5467
15 of 15
71. Foster, E.; Qaseem, A.; Connor, T. Can better mental health services reduce the risk of juvenile justice system involvement? Am. J.
Public Health 2004, 94, 859–865. [CrossRef]
72. Yoder, J.R.; Whitaker, K.; Quinn, C.R. Perceptions of recidivism among incarcerated youth: The relationship between exposure to
childhood trauma, mental health status, and the protective effect of mental health services in juvenile justice settings. Adv. Soc.
Work 2017, 18, 250–269. [CrossRef]
73. Berger, K.S. The Developing Person: Through Childhood and Adolescence; Worth Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005.
