REHABILITATION
July 2018. Vol 19. Num 2
Research Paper: The Effect of Family-Centered Nature Therapy on Children With
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Maryam Ramshini1, *Saeid Hasanzadeh2, Gholam Ali Afroz2, Hadi Hashemi Razini3
1. Department of Psychology, Faculty of Literature Humanities and Social Sciences, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.
2. Department of Psychology and Education of Exceptional Children, Faculty of Psychology and Education, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran.
3. Department of General Psychology, Faculty of Psychology and Education, Kharazmi University, Tehran, Iran.
Use your device to scan
and read the article online
Citation: Ramshini M, Hasanzadeh S, Afroz GhA, Hashemi Razini H. [The Effect of Family-Centered Nature Therapy on Children
With Autism Spectrum Disorder (Persian)]. Archives of Rehabilitation. 2018; 19(2):150-159. http://dx.doi.org/10.32598/rj.19.2.150
: http://dx.doi.org/10.32598/rj.19.2.150
Received: 08 Oct 2017
Accepted: 09 Feb 2018
Keywords:
Nature therapy,
Family-centered,
Autism
ABSTRACT
Objective The treatment of autism, a long-term developmental neurological disorder, is controversial. Because
of the increasing trend and the lack of a known cause in this area, the treatment is complicated; obscure devel-
opment of the disorder is a fundamental issue for the parents of these children. Due to the nature of the disor-
der and involvement of long durations of treatment, various therapeutic methods are used. In addition to the
present treatments, a cost-effective and effective treatment is nature therapy (Eco therapy). Therefore, we de-
cided to study the effectiveness of family-centered nature therapy on children with autism spectrum disorder.
Materials & Methods A quasi-experimental (pre-test/post-test) study was conducted involving children with
autism spectrum disorder (3-7 years old) who were referred to Tehran’s rehabilitation and therapeutic centers.
Fourteen children with autism spectrum disorder were selected by an available sampling method and ran-
domly assigned to experimental and control groups. In each group, 7 children (6 boys and 1 girl) were placed.
Ten therapeutic sessions were conducted in 3 months in the summer of 2017; each session was held for 3 hours
(9 am to 12 pm) in the Nature School of Savan (located in Chitgar Forest Park) with the obligatory presence of
parents (parents or at least one of them). To collect data, the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC) and
the Nature Therapy programs (based on the theoretical framework and relevant research findings) were used.
The Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC) consisting of four parts, speech / language / communication,
socialization, sensory / cognitive awareness, and health / physical / behavior were scrutinized three times,
i.e., before the start of the session, 10 days after the last session of education and three months after the last
training session. Each family was followed up by the other families. The variables studied in this study were,
family-centered nature therapy (independent variable) and autism spectrum disorder syndrome (dependent
variable). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistical methods (mean, standard deviation, minimum and
maximum scores) and inferential methods (Leven test to assess the assumption of the equation of error vari-
ances, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to examine the normal distribution of covariance analysis and to investigate
the effect of test conditions on the dependent variable of the groups).
Results The results showed that the average score of the post-test for Autism Treatment increased in the experi-
mental group (172.3±5.11) compared with the post-test for control (1.151±10.24), which was statistically sig-
nificant. This showed that the nature therapy program brought an improvement in children with autism spec-
trum disorder. Also, the average follow-up scores (after 3 months) of the experimental group (173.91±12.02)
indicated the efficacy of treatment. The results of covariance analysis indicated that the calculated F value
(F=21.91) was highly significant (P<0.001), indicating the effectiveness of the experimental conditions on the
dependent variable (improvement in syndrome).
Conclusion The findings of this study showed that family-centered nature therapy improved the syndrome in
children with autism spectrum disorder. These children have shown remarkable progress, especially in the field
of social and communication skills. Therefore, it is suggested that this type of treatment has positive, simple and
accessible effects and can be used as a complementary method along with other treatments for these children.
* Corresponding Author:
Saeid Hasanzadeh, PhD
Address: Department of Psychology and Education of Exceptional Children, Faculty of Psychology and Education, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran.
Tel: +98 (21) 88802214
E-Mail: shasanz@ut.ac.ir
150

تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم
مریم رامشینی* ،1سعید حس نزاده ،2غلامعلی افروز ،2هادی هاشمی رزینی3
-1گروه روانشناسی ،دانشکده ادبیات علوم انسانی و اجتماعی ،واحد علوم و تحقیقات ،دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی ،تهران ،ایران.
-2گروه روانشناسی و آموزش کودکان استثنایی ،دانشکده روانشناسی و علوم تربیتی ،دانشگاه تهران ،تهران ،ایران.
-3گروه روانشناسی عمومی ،دانشکده روانشناسی و علوم تربیتی ،دانشگاه خوارزمی ،تهران ،ایران.
هدف درمان اتیسم به عنوان اختلال عصبی تحولی طولان یمدت موضوع بح ثانگیزی است .به دلیل روند افزایش و نبود علت شناخت هشده
مشخص در این زمینه ،درمان این اختلال پیچیده و مبهم رشدی ،مسئله اساسی برای والدین این کودکان است .با توجه به نوع اختلال و
مدت طولانی سیر آن ،از رو شهای درمانی گوناگونی استفاده م یشود .یکی از درما نهایی که جزء درما نهای مقرو نب هصرفه و مؤثر است،
طبیع تدرمانی (اکوتراپی) است .با توجه به این مسئله بر آن شدیم که اثربخشی طبیع تدرمانی خانوادهمحور را بر روی نشانگان کودکان
با اختلال طیف اتیسم بررسی کنیم.
روش بررسی این مطالعه به صورت کاربردی و از نوع نیم هآزمایشی (پی شآزمون و پ سآزمون) با گروه کنترل انجام شد .جامعه آماری
پژوهش شامل تمام کودکان 3تا 7سال با اختلال طیف اتیسم م یشد که به مراکز توانبخشی و درمانی شهر تهران مراجعه کرده بودند.
حجم نمونه 14نفر از کودکان با اختلال طیف اتیسم بود که با روش نمون هگیری در دسترس انتخاب و به صورت تصادفی در دو گروه
آزمایش وکنترل جایگزین شدند .در هر گروه (آزمایش و کنترل) 7کودک 6(پسر و 1دختر) قرار گرفت .جلسات طبیع تدرمانی در 10
جلسه به مدت 3ماه در تابستان 1396طی 3ساعت 9(صبح تا 12ظهر) در مدرسه طبیعت ساوان (واقع در پارک جنگلی چیتگر) به
همراه حضور الزامی والدین (پدر و مادر و یا کمترین یک نفر از آ نها) برگزار شد .برای جم عآوری دادهها از فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم
و برنامه طبیع تدرمانی تدوی نشده بر اساس چارچوب نظری و یافت ههای پژوهشی استفاده شد .فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم شامل چهار
قسمت پیشرفت گفتار و زبان و ارتباطات ،اجتماعی شدن،آگاهی حسی و شناختی ،و وضعیت بهداشتی و جسمی و رفتاری است که سه
مرتبه یعنی قبل از شروع جلسات 10 ،روز بعد از آخرین جلسه آموزشی و سه ماه بعد از آخرین جلسه آموزشی به عنوان دوره پیگیری
توسطخانوادههاتکمیلشد.متغیرهایبررس یشدهدراینپژوهش،برنامهطبیع تدرمانیخانوادهمحور(متغیرمستقل)ونشانگاناختلال
طیف اتیسم (متغیر وابسته) بود .دادههای ب هدس تآمده با استفاده از رو شهای آماری توصیفی (میانگین ،انحراف معیار،کمترین و بیشترین
نمرات) و استنباطی (آزمون لون برای بررسی فرض برابری واریان سهای خطا ،آزمون کالموگروف اسمیرنف برای بررسی طبیعی بودن
توزیع ،و تحلیل کوواریانس برای بررسی اثر شرایط آزمایش بر متغیر وابسته نتایج آزمون اثرات بی نگروهی) تجزی هوتحلیل شدند.
یافت هها میانگین نمره پ سآزمون فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم درگروه آزمایشی 172/3با انحراف استاندارد 11/5به دست آمد که نسبت
به میانگین پ سآزمون گروه کنترل برابر با 151/1با انحراف استاندارد 24/10افزایش داشت .این افزایش به لحاظ آماری معن یدار به دست
آمد و نشان داد که برنامه طبیع تدرمانی باعث کاهش نشانگان در کودکان مبتلا به اختلال طیف اتیسم م یشود .همچنین میانگین نمرات
پیگیری گروه آزمایش 173/90با انحراف استاندارد 12/02به دست آمد که نشا ندهنده اثربخشی درمان بعد از 3ماه است .نتایج تحلیل
کوواریانس نشان داد که مقدار 21/90 Fو سطح معناداری 0/001به دست آمد که با توجه به ،0/001≥0/05مقدار Fمحاسب هشده معنادار
شد که بیانگر اثر شرایط آزمایش بر متغیر وابسته (کاهش نشانگان) است.
نتیج هگیری یافت ههای تحقیق نشان طبیع تدرمانی (اکوتراپی) خانوادهمحور باعث کاهش نشانگان در کودکان با اختلال طیف اتیسم
م یشود .این کودکان مخصوصاً در زمینه مهار تهای اجتماعی و ارتباطی پیشرفت قابل ملاحظ های را نشان دادند .بنابرانین م یتوان از
این روش به دلیل تأثیر مثبت ،ساده و در دسترس بودن ،به عنوان روشی مکمل در کنار درما نهای دیگر برای کاهش نشانگان کودکان
با اختلال طیف اتیسم استفاده کرد.
تاریخ دریافت 16 :مهر 1396
تاریخ پذیرش 20 :بهمن 1396
کلیدواژ هها:
طبیع تدرمانی ،اتیسم،
خانوادهمحور
* نویسنده مسئول:
دکتر سعید حس نزاده
نشانی :تهران ،دانشگاه تهران ،دانشکده روانشناسی و علوم تربیتی ،گروه روانشناسی و آموزش کودکان استثنایی.
تلفن+98 )21( 88802214 :
رایانامهshasanz@ut.ac.ir :
151

تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
صحرایی و بیابا نها را دربر م یگیرد که شامل زندگی گیاهان،
حیوانات و عناصر طبیعی مانند آب ،سنگ ،خاک ،شن و غیره
م یشود .طبیع تدرمانی شیوهای است که در محیط ،با استفاده
از عناصر طبیعی موجود در آن به صورت فعالی تها و تجربیات
مختلف محیطی استفاده م یشود .]13[
صحبت درباره طبیع تدرمانی و تأثیر آن بر انسان وکاهش فشار
روانی او در حوزه روانشناسی محیطی ذکر شده است؛ حوزهای که
بخش وسیعی از تحقیقات در زمینه تعامل انسان با طبیعت را
دربر م یگیرد .]14[در این زمینه نظری ههایی وجود دارد که از آن
جمله م یتوان به نظریه بیوفیلیا ،نظریه ترمیم و بازسازی توجه ،و
نظریه دلبستگی و حفظ محیط اشاره داشت.
نظریه بیوفیلیا7
ویلسون 8در سال 1984به عنوان اولین زیس تگرا در این
نظریه عنوان م یکند که بین انسان و دیگر موجودات زنده
پیوندی غریزی وجود دارد؛ یعنی انسا نها به طور تکاملی
خواهان نزدیکی با جهان طبیعت هستند .این نیاز ن هفقط در
بهرهوری مادی ،بلکه در تمام زمین ههای رشد هیجانی ،شناختی،
زیباشناختی و اخلاقی وجود دارد.
نظریه ترمیم و بازسازی توجه
اولین بارکاپلان 9و کاپلان در سال 1989با تمرکز روی فرایند
توجه بیان کردند که طبیعت اثری ترمیمی بر توجه دارد .به
عبارت دیگر ،محیط طبیعی نوع خاصی از عملکرد شناختی را
برای انسان به همراه م یآورد .حضور فرد در طبیعت و وجود
عناصر طبیعی در آن باعث م یشود ذهن وارد مرحله شیفتگی
محض شود و خستگی ناشی از توجه پایدار به یک مسئله را از
بین ببرد؛ یعنی به عنوان نوعی عامل تسهی لکننده عمل کند و
این خود باعث بازسازی ذهن و بالا رفتن سرعت یادگیری شود.
نظریه دلبستگی و حفظ محیط
اینورث )1978( 10و بالبی )1988( 11این نظریه را مطرح
کردند .آ نها بیان کردند که از مزی تهای طبیعت این است که
مردم در آن احساس مالکیت م یکنند و حس مالکیت و تعلق
باعث شک لگیری دلبستگی سالم م یشود .در واقع شکل دادن و
تسهیلدلبستگ یهایهیجانیبههردوجهانانسانیوغیرانسانی
م یتواند باعث ترغیب سلامت روان شود .]14، 15[
این شیوه درمانی دربرگیرنده انواع مختلفی از درما نها است
7. Biophilia
8. Wilson
9. Kaplan
10. Ainsworth
11. Bowlby
مقدمه
اختلال طیف اتیسم اختلالی است که ملا کهای تشخیصی
آن بر اساس پنجمین راهنمای تشخیصی و آماری اختلا لهای
روانی 1به صورت نقصان مداوم ارتباط و تعاملات اجتماعي در
موقعي تهاي مختلف و الگوهاي علايق ،رفتار و فعالي تهاي
تکراري محدود در زمان حال يا گذشته و در اوايل دوران رشد
بروز يافته باشد .]1[
مرکز اطلاعات اختلالات طیف اتیسم 2علائم این طیف را
نقص در ارتباطات کلامی و غیرکلامی ،ناهنجاری تماس چشمی،
ناتوانی در مشارکت در باز یهای تخیلی ،مشکلات پردازش حسی،
دلبستگی شدید و غیرمعمولی به اشیا ،انجام باز یهای تکراری،
حرکات تکراری و کلیش های ،پیروی انعطا فناپذیر از عادات
روزمره ،تخریب روابط دوجانبه هیجانی و اجتماعیو خودآزاري
م يداند .]2[با توجه به آنچه امروز برآورد شده ،شیوع این اختلال
1در 68نفر تخمین زده شده که نسبت به اولین گزارش آماری
در سال 2002افزایش قابل توجهی داشته است .]3[
این کودکان افرادی با عملکردهای ذهنی متفاوت هستند .به
طوری که شیوههای برقراری ارتباط ،تعامل ،رفتار کردن و یاد
گرفتن آ نها با افراد دیگر متفاوت است .با توجه به سیر طولانی
این اختلال و نیازهای چندگانه آ نها هزین ههای مراقبت این
کودکان بار اقتصادی زیادی برای خانوادهها و جامعه فراهم م یکند
که بخش بیشتر این هزین هها صرف آموزش و درما نهای خاص
م یشود .]4[این مسئله چال شهای زیادی در ارتباط با مراقبت و
مدیریت ب هویژه در زمینه مداخله و درمان برای خانواده و مراقبان
آ نها برای اتخاذ رفتار مقتضی مبتنی بر اطلاعات صحیح فراهم
آورده است .]5[
بحث درمان این کودکان با توجه به شدت و مزمن بودن
اختلال دربرگیرنده شیوههای مختلفی است که ازجمله م یتوان
به تحلیل رفتار کاربردی ،3نظام برقراری ارتباط با استفاده از تبادل
تصویر ،4داستا نهای اجتماعی ،5آموزش و تربیت کودکان دارای
اتیسم و ناتوانی ارتباطی 6اشاره کرد که هزین ههای زیادی را برای
خانوادهها متحمل م یکند .]6-11[
یکی دیگر از مداخلاتی که روشی موفق و مقرو نب هصرفه
است ،روش طبیع تدرمانی (اکوتراپی) است .این مداخله در
میان مردم با طیف وسیعی از نیازها به کار رفته است .]12[
واژه «طبیعت ،»طیف وسیعی از فضاهای باز ،از با غها تا نواحی
1. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM-5)
2. Autism Spectrum disorder Information center (SPIC)
3. Applied behavioral analysis
4. Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS)
5. Social stories
6. Treatment and Education of Autistic and related Communication
Handicapped Children (TEACCH)
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران .تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»
152

تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
با توجه به مطالعات انجا مشده ،در این پژوهش به دنبال بررسی
این مسئله هستیم که برنامه طبیع تدرمانی خانوادهمحور بر
نشانگان کودکان با اختلال طیف اتیسم چه تأثیری دارد؟
روش بررسی
این مطالعه به صورت نیم هآزمایشی (پی شآزمون و پ سآزمون
و پیگیری) با گروه کنترل انجام شد .جامعه آماری پژوهش شامل
تمام کودکان 3تا 7سال های بود که به مراکز توانبخشی و درمانی
شهر تهران مراجعه کرده و توسط روانپزشک مرکز ،تشخیص
اوتیسم را گرفته بودند .پس از تماس تلفنی با مراکز و بیان شرایط
خاص پژوهش مبنی بر حضور الزامی والدین در تمام جلسات
آموزشی ،درنهایت با سه مرکز هماهنگ یهای لازم به عمل آمد.
نمون های شامل 14کودک 12(پسر و 2دختر) به صورت در
دسترس با تشخیص اتیسم بدون ناتوانی ذهنی و نقص توجه و
بی شفعالی انتخاب شدند که والدین آ نها حاضر به شرکت الزامی
در طرح پژوهشی بودند .این افراد به صورت غیرتصادفی در دو
گروه 7نفره 6(پسر و 1دختر) آزمایشی و کنترل قرار گرفتند.
ملا کهای خروج از مطالعه شامل وجود هرگونه اختلال بارز
دیگری غیر اوتیسم که بتواند به عنوان تشخیص اصلی مطرح
شود ،غیبت بیش از دو جلسه و وجود بیماری جسمی بود .این
کودکان هنگام شروع طرح پژوهشی ،مداخلات روانشناسی و
کاردرمانی ذهنی در مرکز را دریافت م یکردند و تا پایان طرح
همچنان مداخلات قبلی خود را ادامه دادند.
تعداد جلسات آموزشی 10جلسه بود که طی 3ماه به مدت
3ساعت در مدرسه طبیعت سیار ساوان واقع در پارک جنگلی
چیتگر تهران برگزار شد .اولین جلسه توجیهی گروه آزمایشی در
تیرماه 1396در ساختمان مرکز بهداشت صداوسیما ،با حضور
پزشک متخصص کودکان مرکز بهداشت و کارمندان آنجا برگزار
شد .بعد از گرفتن رضایت از والدین و مطرح کردن نکات اخلاقی
پژوهش مبنی بر رازداری اطلاعات خصوصی و ارائه نتایج پژوهش
در صورت تمایل آ نها 10 ،جلسه آموزشی در فضای طبیعت
برگزار و در هر جلسه طبق آنچه در جدول شماره 1آمده است
تکالیف انجام شد.
قبل از شروع طرح ،از والدین هر دو گروه (گروه کنترل و
آزمایش) خواسته شد که فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم]23[ 20
را به عنوان پی شآزمون تکمیل کنند .روند جلسات آموزشی به
گون های بود که به خاطر حضور گروهی تمام کودکان به همراه
خانوادهها در طبیعت و همچنین برای ایجاد حس امنیت برای
خانوادهها وکودکان ،محقق از چندین تسهیلگر مدرسه طبیعت
درخواست همکاری کرد .به طوری که در ابتدای هر جلسه
آموزشی محقق تکالیف مربوط به همان جلسه را برای تسهیلگران
20. Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC)
که شامل درمان به کمک حیوان ،12باغبان یدرمانی،13کشاورزی،14
فعالیت هنری در طبیعت ،15بیابا ندرمانی ،16ماجراجوی یدرمانی17
و درمان به کمک تمری نهای سبز 18است .]16، 17[بیشتر
مطالعاتی که امروزه در زمینه طبیع تدرمانی انجام شده ،روی
کودکان با اختلال نقص توجه و بی شفعالی ،بیماران بیمارستانی،
افراد مضطرب و افسرده و پرخاشگر صورت گرفته است .]15، 18[
در تمام این مطالعات ارتباط و تعامل با طبیعت اثرات مثبتی
بر ترویج سلامت ،جلوگیری از بیماری ،بهبود وضعیت جسمانی،
بهبود استرس یا خستگی ذهن ،بهبود کلی و درازمدت در افراد از
نظر سلامت و خوب بودن ،گسترش مهار تهای ارتباطی ،افزایش
عزت نفس ،بهبود ظرفی تهای مختلف رشد شناختی و جسمانی
و اجتماعی و هیجانی کودکان ،کمک به حفظ محیط زیست،
داشتن فرصت برای پرورش گیاه و حیوان ،تعامل با سیستمی
پویا از طریق تغییر فصل ،مشاهده طبیعت به عنوان عاملی
آرام شبخش و اثر انتقال آن به فرد ،دسترسی بالقوه به محصولات
باغ ،انجام و شرکت در کار تیمی ،شرکت در تولید از طریق انجام
فعالی تهای معنی دار اما نه به صورت الزام ،م یگذارد .به عبارت
دیگر حضور در طبیعت و تعامل با عناصری مانند خاک ،گیاه،
درخت ،حیوان ،و باد به عنوان مرکزی برای برگشتن به تعادل
عاطفی و روانی و حفظ و نگهداری حال تهای خل قوخوی مثبت
در نظر گرفته م یشود .]19[
از دیگر مزی تهای طبیع تدرمانی م یتوان به این مسئله اشاره
کرد که این شیوه نوعی خوددرمانی هم محسوب م یشود؛ چرا
که اسباب تحریکات حسی ،بالابردن ظرفیت توجه و دقت ،ایجاد
احساس امنیت ،افزایش حس نشاط ،کاهش استرس و خستگی
روانی ،افزایش احساس خوب بودن را برای فرد فراهم م یسازد .]20[
نداشتن ارتباط با طبیعت و یا عدم فعالیت کودکان در فضای
طبیعی و درگیر شدن آ نها با ابزار و رسان ههای الکترونیکی باعث
ایجاد مشکلی به نام «غفلت از طبیعت» م یشود .ریچارد لو19
این اصطلاح را برای اولین بار در سال 2005مطرح کرد و بیان
داشت که این مشکل بر سبک و کیفیت زندگی کودکان تأثیر
م یگذارد .]21[لذا آگاه کردن کودک و والدین از وجود موهبت
طبیعت و بیدار کردن شور و شوق حضور و بازی در طبیعت برای
آ نها امکان تجربه بیشتر طبیعت را برای کودک به همراه دارد و
در نهایت منجر به ه مآغوشی بیشتر طبیعت ،کودک و والدین و
بهتر شدن روحیه آ نها م یشود .]22[
12. Animal assisted intervention
13. Horticultural therapy
14. Farming
15. Doing art in or with nature
16. Wilderness therapy
17. Adventure therapy
18. Green exercise therapy
19. Richard Louv
153
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران.تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»

تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
دانشگاه علوم وتحقیقات تهران و مرکز بهداشت صداوسیمای
تهران این پژوهش را تأیید کردهاند .در جدول شماره 1تکالیف
آموزشی هر جلسه آورده شده است.
ابزارهای مورد استفاده در پژوهش عبارتنداز:
فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم21
ریملند و ادلسون )1993(این فهرست را طراحی کردند.
21. Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC)
و خانوادهها توضیح م یداد و بعد آموزش را شروع م یکرد.
هر کدام از والدین موظف بودند که در یک سری از تکالیف
جلسه با تسهیلگر و فرزند خود همراه باشند .در بعضی موارد مادر
یا پدر ب هتنهایی و با فرزند خود (بدون وجود تسهیلگر) تکلیف
خواست هشده را به اتمام رساندند 10 .روز پس از پایان جلسات
آموزش ،گروه آزمایش و کنترل مجدداً فهرست ارزیابی درمانی
اتیسم ]23[را به عنوان پ سآزمون تکمیل کردند .پس از 3ماه
نیز گروه آزمایش آن را به عنوان مرحله پیگیری تکمیل کرد.
تکالیف انجا مشده
جدول .1تکالیف آموزشی مربوط به جلسات طبیع تدرمانی
جلسات
بودن در طبیعت بدون انجام فعالیت (علاق همند شدن و درگیری ذهنی کودک به طبیعت بدون هدایت مستقیم مربی)
انجام فعالی تهایی مانند نشستن روی چمن ،درازکشیدن روی چمن ،نشستن روی زمین ،نشستن کنار جوی آب ،نشستن زیر سایبان ،قدم زدن در
محیط طبیعی ،تکیه دادن به درخت
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
ایجاد جادههای فرضی روی زمین و راه رفتن کودک در مسیر مشخ صشده و برداشتن کا جهای گذاشت هشده در جاده و انداختن آ نها در نایلون،
پوشاندن بدن در زیر خاک و گل ،راه رفتن روی چمن و خاک با پای برهنه و بدون کفش ،درست کردن نان به صورت ابتدایی و خوردن آن (که
ملاک بیشتر ورز دادن آرد و آب با هم بود ،)انجام حرکات تعادلی (تاب بازی کردن) از طریق طنابی که به دو درخت بسته شد ،ایجاد مانع تونلی در دو
طرف جوی آب و رد شدن کودکان از زیر تونل ،شستن اجزای بدن در آب ،راه رفتن داخل جوی آب ،انجام حرکات ظریف (خاک بازی و گل بازی،)
لمس حیوان
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
جمع کردن هیزم و کاج و چوب توسط بچ هها و درست کردن آتش و انداختن س بزمینی در آن ،پوست کردن و خوردن س بزمینی ،بوییدن نانی که
روی آتش گرم شده بود ،راه رفتن روی بر گهای خشک ،ارتباط گرفتن و پوشاندن بدن با بر گهای خشک
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
قرار گرفتن بدن در وضعی تهای مختلف در فضا ،انجام حرکات درشت (بالا رفتن از نردبان چوبی و ،)...انجام حرکات تعادلی روی چوب مانند راه
رفتن ،دراز کشیدن روی چمن و سکوت کردن ،لمس و گرفتن حیوان ،درست کردن ِگل و گذاشتن آن روی پوست دست و پا و بدن
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
انجام بازی هف تسنگ ،انجام باز یهای مختلف با توپ ،انجام بازی مشابه بولینگ با قطعات چوب ،دراز کشیدن و غلت زدن روی چمن ،پنهان کردن
بدن زیر شن و سنگ ریزه ،درست کردن آتش و پختن املت توسط والدین
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
تماس کل سطح بدن کودک با برگ خشک ،ترسیم اشکال مختلف با استفاده از گل ،انجام حرکات درشت مثل پریدن و دویدن و ،...جمع کردن
سن گهای ریز و درشت و برگ از روی چمن ،غذا دادن به حیوان ،درست کردن میرزاقاسمی روی آتش توسط والدین
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
تکیه دادن پشت به درخت و خاراندن پشت به وسیله درخت ،نشستن در کنار جوی آب و شنیدن صدای جریان آب ،قرار گرفتن بدن در وضعی تهای
مختلف در فضا ،انجام حرکات تعادلی مانند :ایستادن روی یک پا ،روی پاشنه راه رفتن و ،...ساخت وسایل مختلف روی خاک و شن با استفاده ازچوب
و سنگ و ،...پختن سی بزمینی و درست کردن چای روی آتش توسط والدین
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
آب دادن به باغچه گل با استفاده از شلنگ ،کندن سبزی از روی درخت ،بو کشیدن سبزی ،بالا رفتن از تور عنکبوتی برای انجام حرکات تعادلی
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
دراز کشیدن روی زمین و پوشاندن بدن کودک با استفاده از سنگ و شن (توسط محقق و پژوهشگر ،)راه رفتن روی لب ههای سنگی کنار باغچه ،کندن
سبزی از باغچه ،آب دادن به بوته گوج هفرنگی با استفاده از لیوان (کودک باید لیوان را از داخل جوی آب پر م یکرد و بدون اینکه آب لیوان بریزد ،آن
را روی سبز یها و ...م یریخت ،)پختن سی بزمینی و بلال روی آتش
تکرار جلسه قبل و حضور در طبیعت همراه با انجام فعالی تهای خاص .فعالی تها شامل:
رفتن به داخل قفس پرنده و خرگوش و بغل گرفتن و غذا دادن به آ نها ،بالارفتن از نردبان طنابی آویزا نشده به درخت برای انجام حرکات تعادلی،
بوییدن چوب سوخته و نان ،درست کردن نان (مخلوط کردن آرد و آب و ورز دادن خمیر ،)پختن جوج هکباب توسط والدین
اولین جلسه
دومین جلسه
سومین جلسه
چهارمین جلسه
پنجمین جلسه
ششمین جلسه
هفتمین جلسه
هشتمین جلسه
نهمین جلسه
دهمین جلسه
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران .تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»
154
تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
صورت آزاد و بدون هدایت مستقیم محقق صورت گرفت .مرحله
دوم شامل سه بخش انجام فعالیت مربوط به باغبان یدرمانی،
ارتباط با حیوان در محیط طبیعی و انجام فعالی تهای فیزیکی
در محیط طبیعی بود که در هر بخش تکالیف خاصی جایگزین
شدند .بخش «انجام فعالی تهای فیزیکی در محیط طبیعی»
دربرگیرنده شش نوع فعالیت بود که هر کدام مربوط به یکی
از حواس مختلف (بینایی ،چشایی ،لامسه ،شنوایی ،بویایی) به
همراه حس وستیبولار تنظیم شد 5 .نفر از متخصصان مربوطه
روایی محتوای برنامه را تأیید کردند .در تمام این بخ شها شواهد
پژوهشی به لحاظ استناد برنامه لحاظ شد.
یافت هها
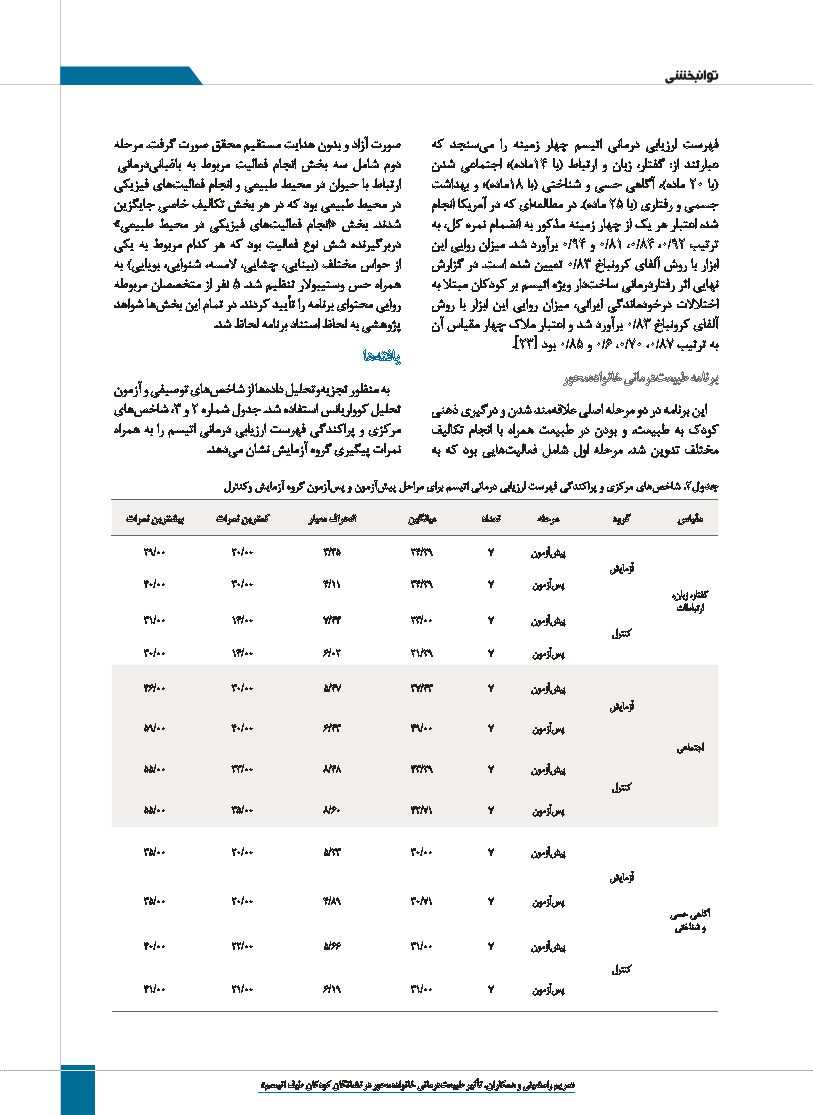
به منظور تجزی هوتحلیل دادهها از شاخ صهای توصیفی و آزمون
تحلیل کوواریانس استفاده شد .جدول شماره 2و ،3شاخ صهای
مرکزی و پراکندگی فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم را به همراه
نمرات پیگیری گروه آزمایش نشان م یدهد.
فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم چهار زمینه را م یسنجد که
عبارتند از :گفتار ،زبان و ارتباط (با 14ماده)؛ اجتماعی شدن
(با 20ماده ،)آگاهی حسی و شناختی (با 18ماده)؛ و بهداشت
جسمی و رفتاری (با 25ماده .)در مطالع های که در آمریکا انجام
شد ،اعتبار هر یک از چهار زمینه مذکور به انضمام نمره کل ،به
ترتیب 0/81 ،0/84 ،0/92و 0/94برآورد شد .میزان روایی این
ابزار با روش آلفای کرونباخ 0/83تعیین شده است .در گزارش
نهایی اثر رفتاردرمانی ساخ تدار ویژه اتیسم بر کودکان مبتلا به
اختلالات درخودماندگی ایرانی ،میزان روایی این ابزار با روش
آلفای کرونباخ 0/83برآورد شد و اعتبار ملاک چهار مقیاس آن
به ترتیب 0/6 ،0/70 ،0/87و 0/85بود .]23[
برنامهطبیع تدرمانیخانواد همحور
این برنامه در دو مرحله اصلی علاق همند شدن و درگیری ذهنی
کودک به طبیعت ،و بودن در طبیعت همراه با انجام تکالیف
مختلف تدوین شد .مرحله اول شامل فعالی تهایی بود که به
جدول .2شاخ صهای مرکزی و پراکندگی فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم برای مراحل پی شآزمون و پ سآزمون گروه آزمایش وکنترل
بیشترین نمرات
کمترین نمرات
انحراف معیار
میانگین
تعداد
مرحله
گروه
مقیاس
29/00
20/00
3/35
24/29
7
پی شآزمون
آزمایش
40/00
30/00
4/11
34/29
7
پ سآزمون
گفتار ،زبان،
ارتباطات
31/00
14/00
7/44
23/00
7
پی شآزمون
کنترل
30/00
14/00
6/02
21/29
7
پ سآزمون
46/00
30/00
5/47
37/43
7
پی شآزمون
آزمایش
59/00
40/00
6/43
49/00
7
پ سآزمون
اجتماعی
55/00
33/00
8/48
43/29
7
پی شآزمون
کنترل
55/00
35/00
8/60
42/71
7
پ سآزمون
35/00
20/00
5/23
30/00
7
پی شآزمون
آزمایش
35/00
20/00
4/89
30/71
7
پ سآزمون
40/00
22/00
5/66
31/00
7
پی شآزمون
آگاهی حسی
و شناختی
کنترل
41/00
21/00
6/19
31/00
7
پ سآزمون
155
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران .تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»
تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
بیشترین نمرات
کمترین نمرات
66/00
32/00
67/00
33/00
64/00
64/00
انحراف معیار
11/46
11/50
7/54
64/00
64/00
7/02
170/0
138/0
11/5
193/0
156/0
11/5
189/0
18/4
15/94
187/0
17/7
24/10
میانگین
51/29
50/33
51/29
50/80
152/7
172/3
151/9
151/1
تعداد
مرحله
7
پی شآزمون
7
پ سآزمون
7
پی شآزمون
7
پ سآزمون
7
پی شآزمون
7
پ سآزمون
7
پی شآزمون
7
پ سآزمون
گروه
مقیاس
آزمایش
کنترل
بهداشت
جسمی و
رفتاری
آزمایش
کنترل
فهرست
ارزیابی درمانی
اتیسم
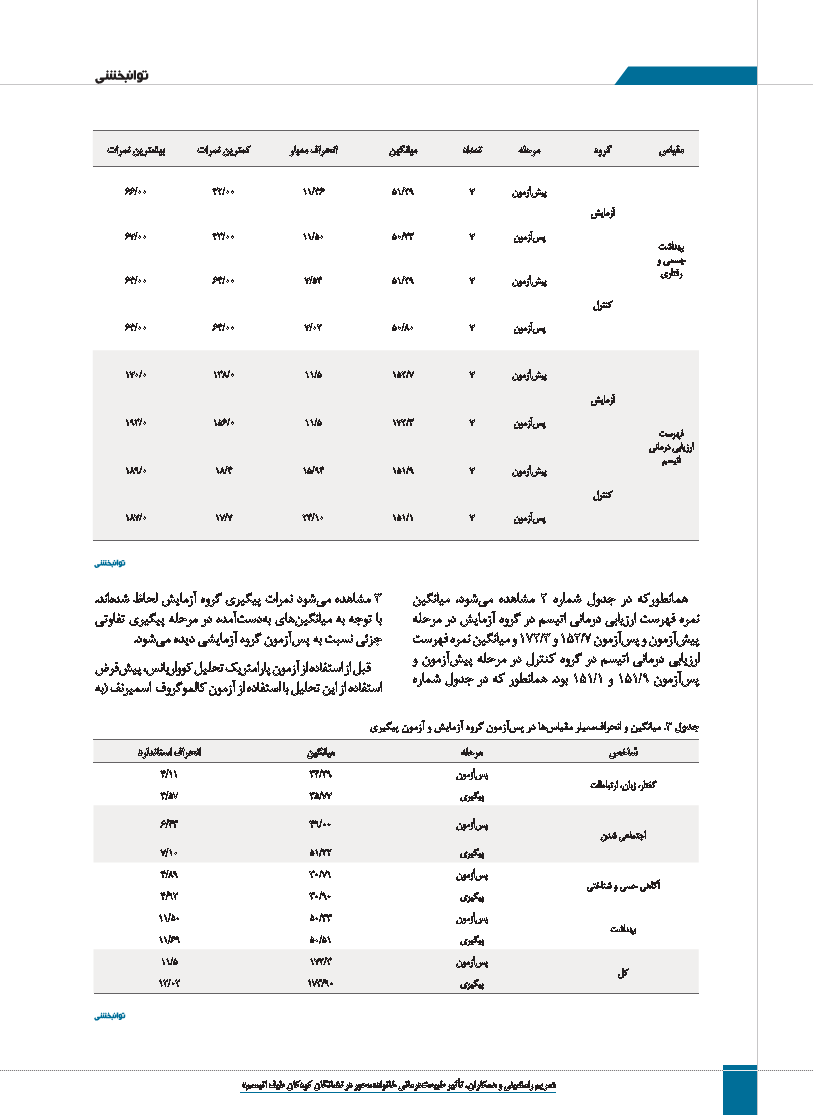
3مشاهده م یشود نمرات پیگیری گروه آزمایش لحاظ شدهاند.
با توجه به میانگی نهای ب هدس تآمده در مرحله پیگیری تفاوتی
جزئی نسبت به پ سآزمون گروه آزمایشی دیده م یشود.
قبلازاستفادهازآزمونپارامتریکتحلیلکوواریانس،پی شفرض
استفاده از این تحلیل با استفاده از آزمون کالموگروف اسمیرنف (به
همانطورکه در جدول شماره 2مشاهده م یشود ،میانگین
نمره فهرست ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم در گروه آزمایش در مرحله
پی شآزمون و پ سآزمون 152/7و 172/3و میانگین نمره فهرست
ارزیابی درمانی اتیسم در گروه کنترل در مرحله پی شآزمون و
پ سآزمون 151/9و 151/1بود .همانطور که در جدول شماره
انحراف استاندارد
4/11
4/57
6/43
7/10
4/89
4/92
11/50
11/69
11/5
12/02
میانگین
34/29
35/77
49/00
51/22
30/71
30/90
50/33
50/51
172/3
173/90
جدول .3میانگین و انحرا فمعیار مقیا سها در پ سآزمون گروه آزمایش و آزمون پیگیری
مرحله
پ سآزمون
پیگیری
شاخص
گفتار ،زبان ،ارتباطات
پ سآزمون
پیگیری
پ سآزمون
پیگیری
پ سآزمون
پیگیری
پ سآزمون
پیگیری
اجتماعی شدن
آگاهی حسی و شناختی
بهداشت
کل
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران .تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»
156
تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
جدول .4نتایج تحلیل کوواریانس در بررسی اثربخشی برنامه طبیع تدرمانی بر نشانگان طیف اتیسم
اتا
سطح معناداری
F
درجه آزادی
منبع شاخص تغییرات مجموع مجذورات
0/67
21/90
1
1460/03
آزمایش
11
733/20
خطا
0/001
13
4228/86
کل
ترشح موجب تحریک مغز میانی و بهبود زندگی هیجانی و ارتباط
بهتر با دیگران م یشود .با توجه به اینکه کودکان اتیسم در زمینه
مهار تهای ارتباطی و هیجانی ضعیف عمل م یکنند ،ارتباط
با گیاهان و طبیعت م یتواند باعث کاهش بعضی نشانگان این
کودکان شود .]24[
تبیین دیگری که م یتوان ارائه کرد نظرات ویلسون است.
ویلسون )1984(معتقد است بین انسان و دیگر موجودات زنده
اطراف او نوعی پیوند غریزی وجود دارد .طوری که به صورت
ژنتیکی و رشد تکاملی خواهان نزدیکی و گرایش ذاتی با طبیعت و
ارتباط برقرار کردن با آن است که باعث رشد زمین ههای هیجانی،
شناختی ،اجتماعی و جسمانی م یشود .]15، 25، 26[احساس
نزدیکی با طبیعت فرصت درگیر شدن فعال با طبیعت و عناصر
آن را بیشتر فراهم م یکند .فعالیت در فضایی مانند محیط
طبیعی به دلیل برقراری ارتباط با عناصر آن مانند حیوان ،آب،
گیاه و تحریک حواس مختلف از طریق رنگ ،صدا و هوا باعث
بهبود وضعیت روانی و اجتماعی م یشود و این مسئله با توجه به
نشانگان کودکان اتیسم م یتواند باعث کاهش مشکلات رفتاری،
اجتماعی ،شناختی و حسی شود .]27[
نکته آخر اینکه ما در طبیع تزدای یترین گوش ههای دنیا با
پدیدهای مواجه هستیم که شاید بتوان آن را اتیسم فرهنگی
نامید .اتیسم فرهنگی به معنای حواس محدودشده ،احساس انزوا
و حب سشدگی است .مطالعات نشان دادهاند که عدم دسترسی به
طبیعت باعث محدود شدن حواس پن جگانه ،دشواری در تمرکز
و توجه ،افزایش بیمار یهای روانی و کاهش روابط و تعاملات
اجتماعی م یشود که تمام ای نها را تحت عنوان «اختلال فقر
طبیعت» نامیدهاند.
جان دیویی به عنوان تأثیرگذارترین معلم آمریکایی در حدود
یک قرن پیش هشدار داده بود که غالب شدن تجربیات ثانویه و غیر
مستقیم در دوران کودکی م یتواند برای او مشکلات زیادی را به
وجود بیاورد ،درصورت یکه تجربه مستقیم طبیعت حواس مختلف
کودک را بیدار م یکند و او را از تجربه دو حسی (بینای یشنوایی)
وسایل الکترونیک رها م یکند .بنابراین طبیعت به عنوان منبع
اصلی و اصیل خورا کرسانی به حواس ،با در اختیار قرار دادن
فضایی آزاد برای جس توجو و درگیری با عناصر و محیط م یتواند
باعث رشد کودک در تمام ابعاد رشدی شود .]22[
منظور بررسی طبیعی بودن توزیع) و آزمون لون (به منظور بررسی
فرض برابری واریان سهای خطا) بررسی شد که نتایج نشان داد
شرایط لازم را برای استفاده از تحلیل کوواریانس دارد.
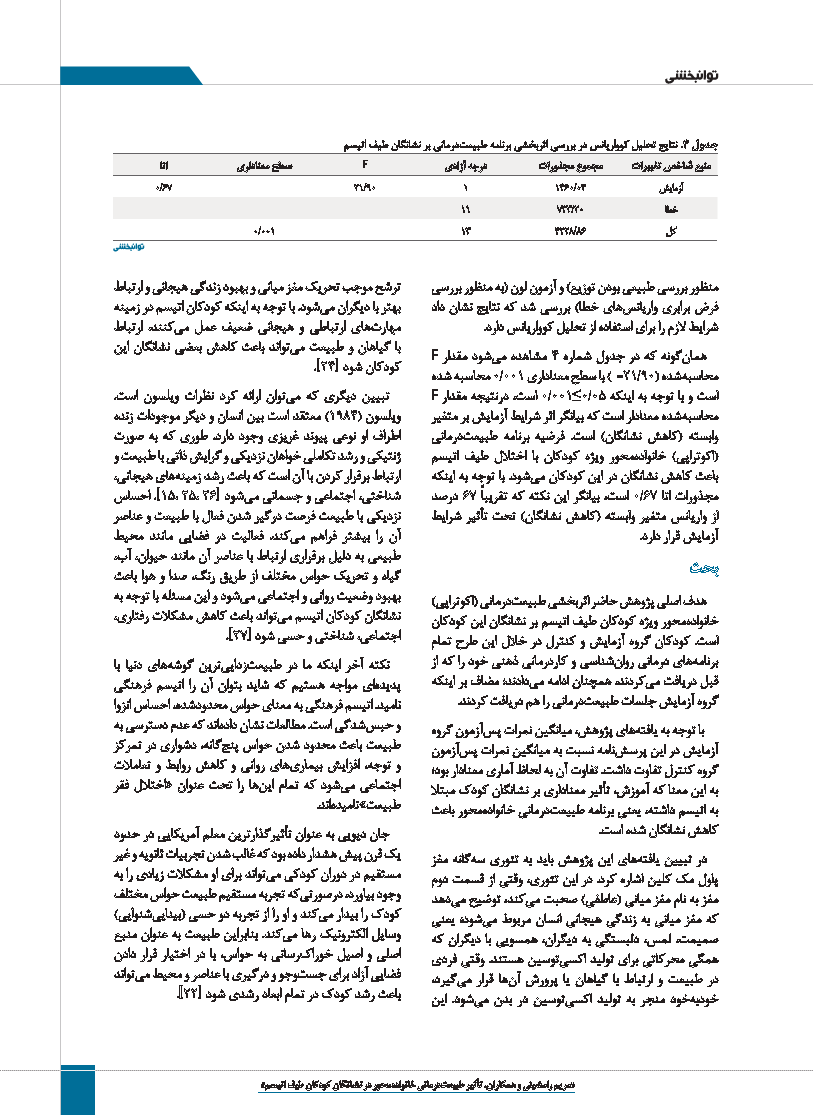
هما نگونه که در جدول شماره 4مشاهده م یشود مقدار F
محاسب هشده )F=21/90(با سطح معناداری 0/001محاسبه شده
است و با توجه به اینکه 0/001≥0/05است ،درنتیجه مقدار F
محاسب هشده معنادار است که بیانگر اثر شرایط آزمایش بر متغیر
وابسته (کاهش نشانگان) است .فرضیه برنامه طبیع تدرمانی
(اکوتراپی) خانوادهمحور ویژه کودکان با اختلال طیف اتیسم
باعث کاهش نشانگان در این کودکان م یشود .با توجه به اینکه
مجذورات اتا 0/67است ،بیانگر این نکته که تقریباً 67درصد
از واریانس متغیر وابسته (کاهش نشانگان) تحت تأثیر شرایط
آزمایش قرار دارد.
بحث
هدف اصلی پژوهش حاضر اثربخشی طبیع تدرمانی (اکوتراپی)
خانوادهمحور ویژه کودکان طیف اتیسم بر نشانگان این کودکان
است .کودکان گروه آزمایش و کنترل در خلال این طرح تمام
برنام ههای درمانی روا نشناسی و کاردرمانی ذهنی خود را که از
قبل دریافت م یکردند ،همچنان ادامه م یدادند؛ مضاف بر اینکه
گروه آزمایش جلسات طبیع تدرمانی را هم دریافت کردند.
با توجه به یافت ههای پژوهش ،میانگین نمرات پ سآزمون گروه
آزمایش در این پرس شنامه نسبت به میانگین نمرات پ سآزمون
گروه کنترل تفاوت داشت .تفاوت آن به لحاظ آماری معنادار بود؛
به این معنا که آموزش ،تأثیر معناداری بر نشانگان کودک مبتلا
به اتیسم داشته ،یعنی برنامه طبیع تدرمانی خانوادهمحور باعث
کاهش نشانگان شده است.
در تبیین یافت ههای این پژوهش باید به تئوری س هگانه مغز
پاول مک کلین اشاره کرد .در این تئوری ،وقتی از قسمت دوم
مغز به نام مغز میانی (عاطفی) صحبت م یکند ،توضیح م یدهد
که مغز میانی به زندگی هیجانی انسان مربوط م یشود؛ یعنی
صمیمت ،لمس ،دلبستگی به دیگران ،همسویی با دیگران که
همگی محرکاتی برای تولید اکس یتوسین هستند .وقتی فردی
در طبیعت و ارتباط با گیاهان یا پرورش آ نها قرار م یگیرد،
خودب هخود منجر به تولید اکس یتوسین در بدن م یشود .این
157
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران .تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»

تابستان . 1397دوره . 19شماره 2
تشکر و قدردانی
این مقاله از رساله دکترای خانم مریم رامشینی از گروه
روانشناسی و آموزش کودکان استثنایی دانشگاه آزاد واحد علوم
وتحقیقات تهران گرفته شده است .مقاله حامی مالی ندارد.
بدی نوسیله از دکتر حمید حسینی (ریاست محترم مرکز
بهداشت صداوسیمای تهران ،)دکتر حسین کریمی (پزشک
متخصص کودکان صداوسیمای تهران ،)خانم زهره ممتازیان
(مدیر مرکز بهداشت صداوسیمای تهران ،)دکتر علیرضا عبدی
(مدیر محترم پارک جنگلی چیتگر ،)خانم ملیحه مرادی و تیم
همراه (مدیر محترم مدرسه طبیعت ساوان) و والدین بزرگواری که
در اجرای این پژوهش صمیمانه همکاری کردند ،تشکر و قدردانی
م یشود.
یافت ههای این پژوهش با نتایج مطالعات تازیکی و همکاران
)2015(مبنی بر تأثیر اس بدرمانی بر افزایش مهار تهای
اجتماعی کودکان مبتلا به اتیسم همسو است .همچنین
با یافت ههای صارمیا نفر و همکاران )2015(مبنی بر تأثیر
اس بسواری در کاهش معنادار شدت بروز اختلافات در تعاملات
اجتماعی کودکان اتیسم ،نتایج پژوهش برگی 22و همکاران
)2016(مبنی بر استفاده از حیوا ندرمانی در بهبود رفتارهای
انطباقی و کوتاه شدن مد تزمان برنام هریزی در حل مسئله
کودکان ،یافت ههای اسمیث 23و همکاران )2016(در خصوص
ورود حیوان به کلا سهای کودکان اتیسم برای کاهش مشکلات
رفتاری ،نتایج مطالعه سیفرت )2014( 24در زمینه اثر مثبت
باغبان یدرمانی روی پیشرفت مهار تهای کودک ،نتیجه پژوهش
پیشگام یادگیری طبیعت )2012( 25در زمینه تأثیر مثبت تماس
روزانه با طبیعت در خصوص کاهش فشار روانی و بهبود روابط
اجتماعی افراد ،و یافت ههای برگر و تایری )2012( 26مبنی بر
استفاده از طبیع تدرمانی (ش ندرمانی) برای بیماران با مشکلات
روانی در زمینه کسب روابط تعاملی بهتر با افراد دیگر در یک
راستا قرار دارد.
نتیج هگیری
بر اساس یافت ههای پژوهش حاضر م یتوان نتیجه گرفت که
برنامه طبیع تدرمانی (اکوتراپی) خانوادهمحور ویژه کودکان
با اختلال طیف اتیسم باعث کاهش بعضی از نشانگان در این
کودکان م یشود.
از محدودیتهای پژوهش حاضر میتوان به فضای مدرسه
طبیعت اشاره کرد .به دلیل اینکه فضای مدرسه طبیعت به
طور کلی برای کودکان عادی تعبیه شده است و از نظر ابزار
و آلات موجود در آن برای کودکان با اختلال طیف اتیسم و
حتی دیگر کودکان با نیاز ویژه به تمهیدات بیشتری نیاز است.
محدودیت دیگر شرایط شغلی والدین کودکان بود که به دلیل
وجود الزامی والدین در تمام جلسات طبیع تدرمانی ،تعداد
جلسات محدود شد.
با توجه به اینکه این برنامه برای کودکان و به دلیل خانوادهمحور
بودن آن برای والدین نتیج هبخش است و باعث بهبود وضعیت
روحی آ نها شد ،پیشنهاد م یشود به عنوان درمان مکمل در
کنار درما نهای دیگر برای کودکان با اختلال طیف اتیسم در
همه سنین و حتی برای کودکانی با نیازهای ویژه استفاده شود تا
شاهد پیشرف تهای بیشتری در تمام ابعاد رشدی کودکان خاص
و سلامت روان بیشتر خانوادههای آ نها باشیم.
22. Borgi
23. Smith
24. Sifret
25. Natural learning initiative
26. Berger and Tiry
«مریم رامشینی و همکاران .تأثیر طبیع تدرمانی خانواد همحور در نشانگان کودکان طیف اتیسم»
158

2 شماره. 19 دوره. 1397 تابستان
References
[1] American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical man-
ual of mental disorders [F Rezaee, et al., Persian trans.]. Tehran:
Arjmand Pub; 2013.
[2] Murphy R. SPICe briefing: Autism spectrum disorder. Edinburgh:
Scottish Parliament Information Centre; 2017.
[3] Russell S, McCloskey CR. Parent perceptions of care received by
children with an autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Pediatric
Nursing. 2016; 31(1):21–31. [DOI:10.1016/j.pedn.2015.11.002]
[4] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). A snapshot
of autism spectrum disorder among 8-year-old children in Multi-
ple Communities across the United States. Atlanta: United States
Department of Health and Human Services; 2014.
[5] Hsiao YJ. Pathways to mental health-related quality of life for par-
ents of children with autism spectrum disorder: roles of paren-
tal stress, children’s performance, medical support, and neighbor
support. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders. 2016; 23:122–
30. [DOI:10.1016/j.rasd.2015.10.008]
[6] Golzari F, Hemati Alamdarloo G, Moradi S. The effect of a social
stories intervention on the social skills of male students with autism
spectrum disorder. SAGE Open. 2015; 5(4):215824401562159.
[DOI:10.1177/2158244015621599]
[7] Morgenthal AH. Child-centered play therapy for children with
autism: A case study (PhD dissertation). Culver City, California:
Antioch University; 2015.
[8] Welterlin A, Turner Brown LM, Harris S, Mesibov G, Delmolino
L. The home teacching program for toddlers with autism. Journal
of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2011; 42(9):1827–35.
[DOI:10.1007/s10803-011-1419-2]
[9] Politte LC, Howe Y, Nowinski L, Palumbo M, McDougle CJ.
Evidence-based treatments for autism spectrum disorder.
Current Treatment Options in Psychiatry. 2015; 2(1):38–56.
[DOI:10.1007/s40501-015-0031-z]
[10] Leaf JB, Leaf R, McEachin J, Taubman M, Ala’i-Rosales S, Ross
RK, et al. Applied behavior analysis is a science and, therefore,
progressive. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.
2015; 46(2):720–31. [DOI:10.1007/s10803-015-2591-6]
[11] Battaglia D, McDonald ME. Effects of the Picture Exchange
Communication System (PECS) on maladaptive behavior in chil-
dren with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD): A review of the
literature. Journal of the American Academy of Special Education
Professionals. 2015; 8:20.
[12] Seifert AR. Cultivating new lives: Anethnographic pilot study of
Eco-therapy provision for people with Alcohol-related problems
in Northern Ireland. Anthropology in Action. 2014; 21(1):4-12.
[DOI:10.3167/aia.2014.210103]
[13] Corazon SS, Stigsdotter UK, Jensen AG, Nilsson K. Develop-
ment of the nature-based therapy concept for patients with stress-
related illness at the Danish healing forest garden Nacadia. Journal
of Therapeutic Horticulture. 2010; 20:33-51.
[14] Plambech T, Konijnendijk van den Bosch CC. The impact of
nature on creativity: A study among Danish creative profession-
als. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening. 2015; 14(2):255–63.
[DOI:10.1016/j.ufug.2015.02.006]
[15] Adams M, Jordan M, Wren J, Wright J. The grow project: A re-
port on the well-being benefits of nature connection for people
with experience of mental distress. Brighton, UK: University of
Brighton, Community and University Partnership Project. 2014.
[16] Sempik J. Green care and mental health: Gardening and farm-
ing as health and social care. Mental Health and Social Inclusion.
2010; 14(3):15–22. [DOI:10.5042/mhsi.2010.0440]
[17] Mind for Better Mental Health. Making sense of ecotherapy [In-
ternet]. 2015. Availble from: https://mhaw.nz/assets/Overseas-
lit-PDFs/making-sense-of-ecotherapy-MIND-2013.pdf
[18] Mustapa ND, Maliki NZ, Hamzah A. Repositioning children’s
developmental needs in space planning: A review of connec-
tion to nature. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015;
170:330-9. [DOI:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.043]
[19] Kahn PH, Kellert SR. Children and nature: Psychological, socio-
cultural, and evolutionary investigations. Cambridge: MIT Press;
2002.
[20] Brown DK, Barton JL, Pretty J, Gladwell VF. Walks4Work: As-
sessing the role of the natural environment in a workplace physi-
cal activity intervention. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environ-
ment & Health. 2014; 40(4):390–9. [DOI:10.5271/sjweh.3421]
[21] McCurdy LE, Winterbottom KE, Mehta SS, Roberts JR. Us-
ing nature and outdoor activity to improve children’s health. Cur-
rent Problems in Pediatric And Adolescent Health Care. 2010;
40(5):102-17. [DOI:10.1016/j.cppeds.2010.02.003]
[22] Louv R. Last child in the woods: Saving our childran from na-
ture-deficit disorder [A Hosseinian, F Azad, Persian trans.]. Teh-
ran: Talangor Pub; 2016.
[23] Pouretemad HR, Khooshabi K. [The effect of autism therapeu-
tic behavioral therapy-Lovaas on children with autistic disorders
(Persian)]. Tehran: Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sci-
ences; 2004.
[24] Haller RL, Kramer CL. Horticultural therapy methods: Con-
necting people and plants in health care, human services, and
therapeutic programs. Abingdon: CRC Press; 2017.
[25] Bagot KL, Allen FC, Toukhsati S. Perceived restorativeness of
children’s school playground environments: Nature, playground
features and play period experiences. Journal of environmental
psychology. 2015; 41:1-9. [DOI:10.1016/j.jenvp.2014.11.005]
[26] Rogerson M, Barton J. Effects of the visual exercise environ-
ments on cognitive directed attention, energy expenditure and
perceived exertion. International Journal of Environmental Re-
search and Public Health. 2015; 12(7):7321-36. [DOI:10.3390/
ijerph120707321] [PMID] [PMCID]
[27] Rat W. Nature and the child (Practical guideline for nature
schools) [AH Vahabzade, Persian trans.]. Mashhad: Sahra Pub;
2016.
159
Ramshini M, et al. The Effect of Family-Centered Nature Therapy on Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. RJ. 2018; 19(2):150-159.
